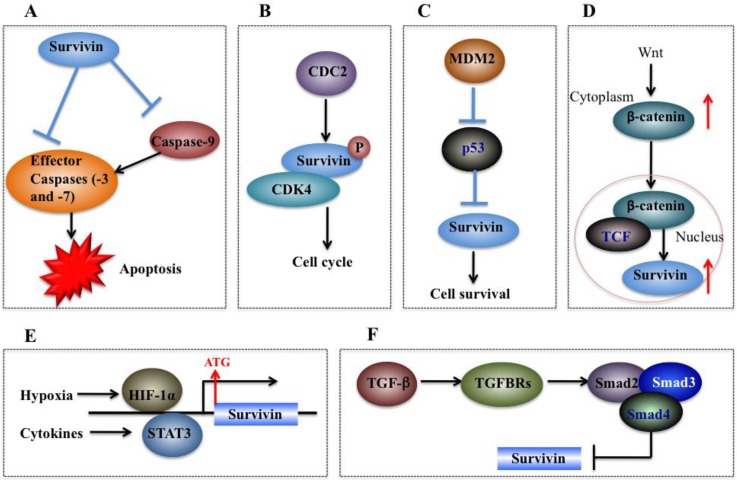
Figure 4.
Molecular mechanisms of survivin in tumorigenesis. (A) Survivin binds and suppresses effector caspases (caspase-3 and 7) and caspase-9, thereby resulting in decreased apoptosis in cancer cells. (B) CDC2 can directly phosphorylate survivin. Survivin also interacts with CDK4, which results in nuclear translocation, thereby leading to S phase shift. (C) Wild-type p53 represses survivin expression at the transcriptional level. (D) Activation of the Wnt signaling pathway leads to accumulation of β-catenin in the cytoplasm, which then translocates to the nucleus to form the β-catenin/TCF enhancer factor transcriptional machinery and upregulate survivin. (E) Both HIF-1α and STAT3 can directly bind to the survivin promoter and function as transcriptional activators of the survivin gene. (F) TGF-β is a negative regulator of survivin. The TGF signaling pathway transcriptionally downregulates survivin expression through a mechanism dependent on Smads 2, 3, and 4.