Fig. 1.
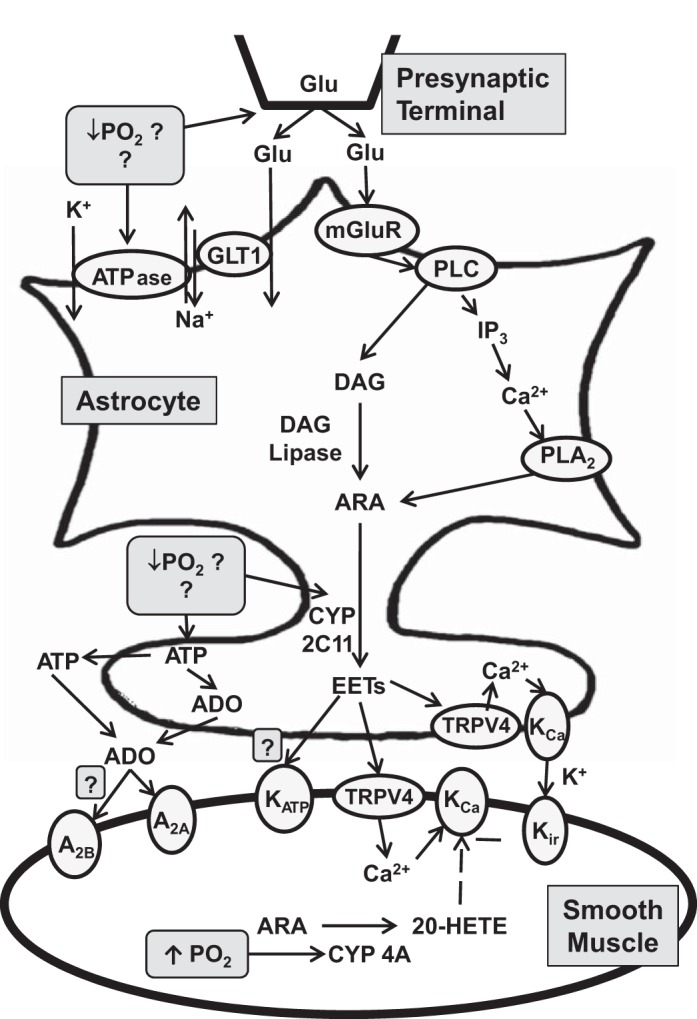
Schematic diagram of possible signaling mechanisms in astrocytes and vascular smooth muscle that result in cerebrovascular vasodilation during hypoxemia. ADO, adenosine; ARA, arachidonic acid; DAG, diacylglycerol; GLT1, primary astrocytic glutamate transporter; Glu, glutamate; IP3, inositol triphosphate; mGluR, metabotropic glutamate receptor; PLA2, phospholipase A2; PLC, phospholipase C; CYP, cytochrome P-450; EET, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; TRPV4, transient receptor potential vanilloid 4; KCa, calcium-activated K+; Kir, inwardly rectifying K+ channel; 20-HETE, 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid. Dashed line indicates negative effect.
