Figure 2.
Effect of the G4-Interacting Compound PDS on Telomere Fragility and Viability of Brca-Deficient MEFs
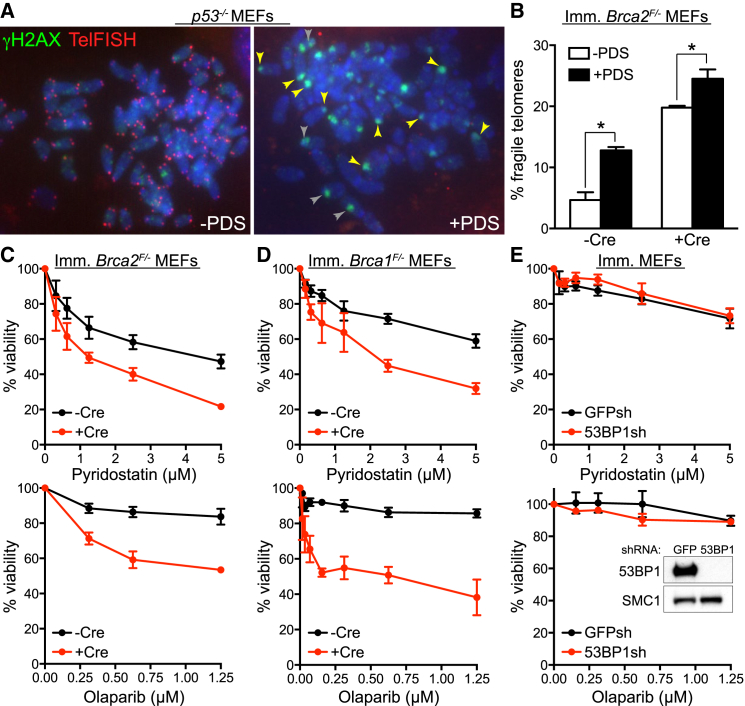
(A) Mitotic chromosome spreads of p53−/− MEFs grown in the presence (+PDS) or absence (−PDS) of 5 μM PDS for 48 hr. Preparations were fixed and stained with anti-γH2AX monoclonal antibody (green). Telomeres were visualized with a Cy3-conjugated (CCCTAA)6-PNA probe (red), using identical exposure conditions for untreated and PDS-treated cells. DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue).
(B) Quantification of fragile telomeres visualized by FISH on metaphase chromosomes from Brca2F/- MEFs treated with Cre (+Cre) and control (−Cre) retroviruses incubated with 5 μM PDS for 40 hr (n = 2; > 1,500 long-arm telomeres were scored per condition per replica; error bars, SD). p values were calculated using an unpaired two-tailed t test (∗p ≤ 0.05).
(C) Dose-dependent viability assays of Brca2F/- MEFs treated with Cre (+Cre) and control (−Cre) retroviruses exposed to PDS or olaparib at the indicated concentrations.
(D) Dose-dependent viability assays of Brca1F/- MEFs treated as in (C).
(E) Dose-dependent viability assays of immortalized (imm.) MEFs treated as in (C) with retroviruses encoding shRNA against GFP or 53BP1 (Bouwman et al., 2010). Cell extracts were immunoblotted as indicated. SMC1 was used as a loading control. See also Figures S1 and S2. Graphs shown are representative of at least two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. Error bars represent SD of triplicate values obtained from a single experiment.