Figure 3.
2p Ab Induces Dimerization of BRCT-Ab2p Complex
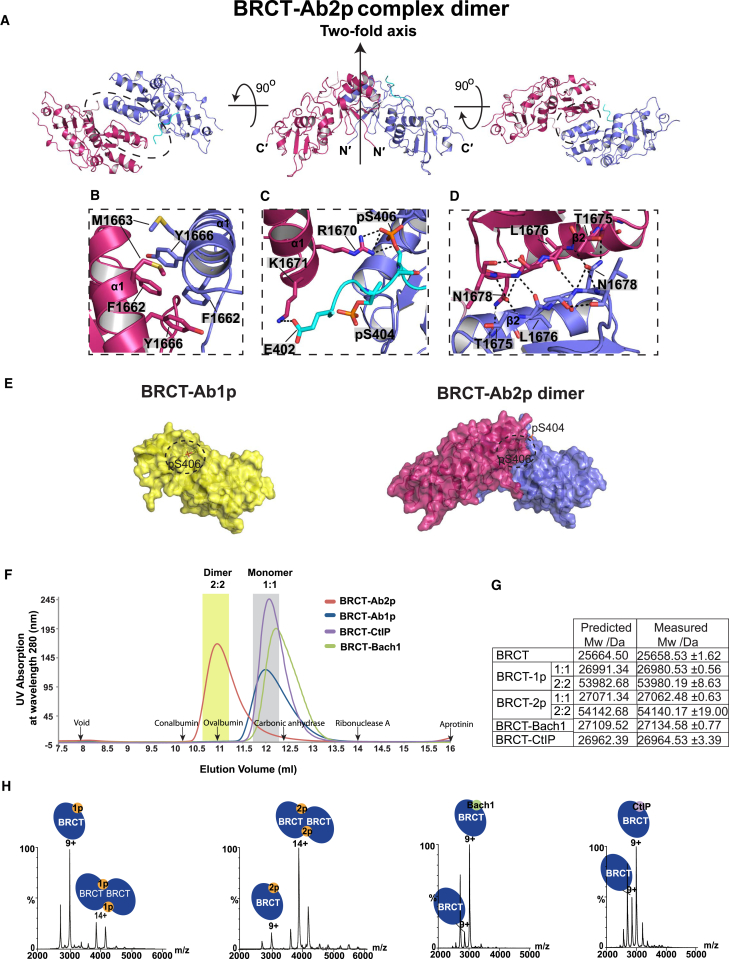
(A) Crystal structure of BRCT-Ab2p complex dimer viewed from three different directions with a two-fold axis. The dimer interface is within the dashed circles and zoomed in (B)–(D).
(B) Dimer interface between two BRCT α1 helices.
(C) Interaction between BRCT α1 helix and Ab2p.
(D) Dimer interface between two BRCT β2 strands. The polar interactions between labeled residues are shown in black dashed lines. The key residues are indicated in the image.
(E) Surface representation of BRCA1-1p_short (yellow) and BRCT-Ab2p dimer (blue and pink). The Abraxas pS406 binding region is indicated in the dashed circle.
(F) Gel filtration BRCT in complex with Ab1p, Ab2p, Bach1, and CtIP phosphopeptides at a concentration of 40 μM (1 mg/ml). The regions for dimer complex (2:2 complex) and monomer complex (1:1 complex) are high lined in yellow and gray shades. The elution positions for void and protein markers aprotinin (Mw = 6,500 Da), ribonuclease A (Mw = 13,700 Da), carbonic anhydrase (Mw = 29,000 Da), Ovalbumin (Mw = 44,000 Da), and Conalbumin (Mw = 75,000 Da) are indicated.
(G) The molecular weight of BRCT and its complexes with phosphopeptide, measured using native mass spectrometry.
(H) The native mass spectra of BRCT-Ab1p, BRCT-Ab2p, BRCT-Bach1, and BRCT-CtIP complexes tested at 15 μM (see also Figures S3 and S4).