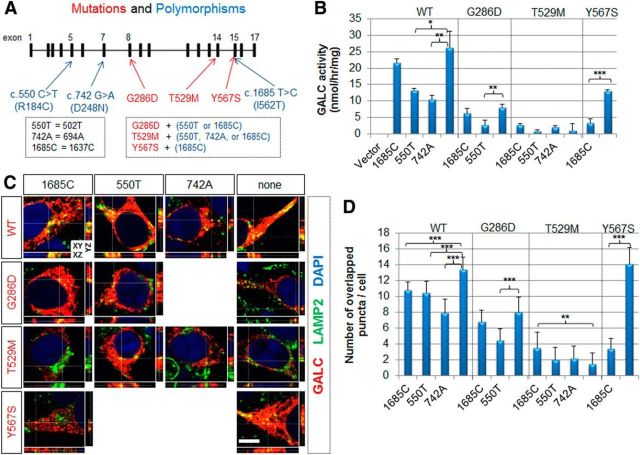
Figure 2.
Benign cis-polymorphisms affect total enzymatic activity and trafficking of GALC. A, Diagram of the genomic structure of GALC and common benign polymorphisms (blue) found in GLD patients. A new numbering classification, starting from the upstream translational start site, was used to define the residue numbers. The G286D later-onset mutation is always found with the c.550T or c.1685C polymorphism. The T529M infantile-onset mutation is always found with the c.550T, c.742A, or c.1685C polymorphism. The Y567S infantile-onset mutation is always found with the c.1685C polymorphism. These three common polymorphisms were introduced by site-directed mutagenesis. B, GALC activities were measured in total lysates prepared from cells transfected with wild-type or mutant GALC in combination with indicated cis-polymorphisms. Both c.550T and c.742A reduced WT GALC activity, whereas only c.550T or c.1685C reduced G286D or Y567S activity, respectively. Error bars indicate SD of triplicates. *p < 0.05 (Student's t test). **p < 0.01 (Student's t test). ***p < 0.001 (Student's t test). C, HEK-293T cells transfected with WT or mutant GALCs in combination with indicated cis-polymorphisms were costained for GALC (red) and LAMP2 (green). Nuclei were labeled with DAPI. Orthogonal views (XY, XZ, and YZ) of a z-stack. White lines indicate section positions. D, Quantification of colocalized GALC and LAMP2 signals was obtained by counting the number of yellow puncta. C, D, All polymorphisms reduced lysosomal targeting of WT GALC. The c.550T and c.1685C polymorphisms reduced lysosomal targeting of G286D and Y567S, respectively. More than three independent experiments were performed with qualitatively similar results. Quantification was performed on 8–16 cells. Error bars indicate SD. **p < 0.01 (Student's t test). ***p < 0.001 (Student's t test). Scale bar: C, 5 μm.