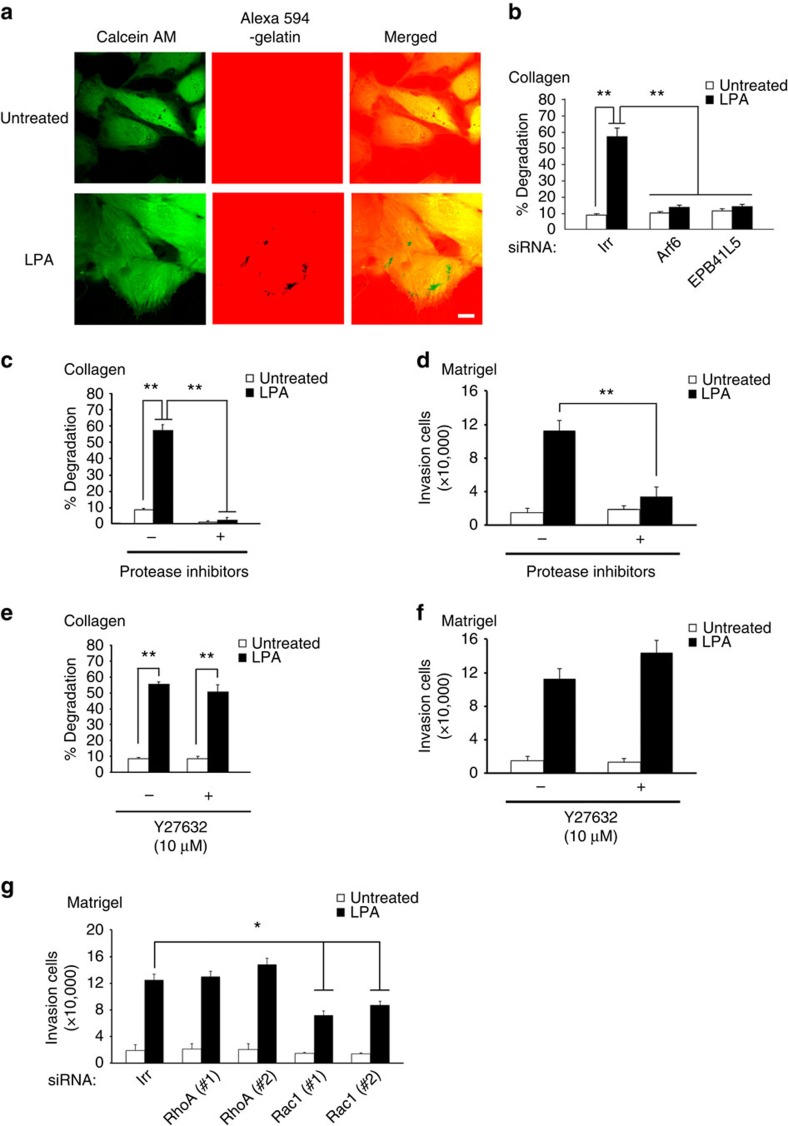
Figure 2. Properties of LPA-induced invasion of 786-O cells.
(a) Invadopodia formation on LPA stimulation. Cells were visualized using calcein AM, and areas of degradation of cross-linked Alexa 594-labelled collagen gels were shown as colourless areas (black dots in the middle panel). Scale bar, 10 μm. (b) Involvement of Arf6 and EPB41L5 in invadopodia formation. Cells were pretreated with siRNAs for Arf6, EPB41L5 or an irrelevant sequence (Irr), before being subjected to the invadopodia formation assay with or without LPA. (c–f) Protease inhibitors (c,d), but not Y27632 (e,f), block LPA-induced matrix degradation (c,e) and Matrigel invasion (d,f). Inhibitors were applied to the cells 6 h before the experiments and were present during the experiments. (g) RhoA, but not Rac1, is dispensable for LPA-induced invasion. Cells were pretreated with siRNAs for RhoA, Rac1 or Irr, before being subjected to the Matrigel invasion assay with or without LPA. (b,c,e) Percentages of cells exhibiting invadopodia are shown as % degradation. (b and c–g) Error bars represent the mean±s.e.m., n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. Statistical analyses were performed using analysis of variance.