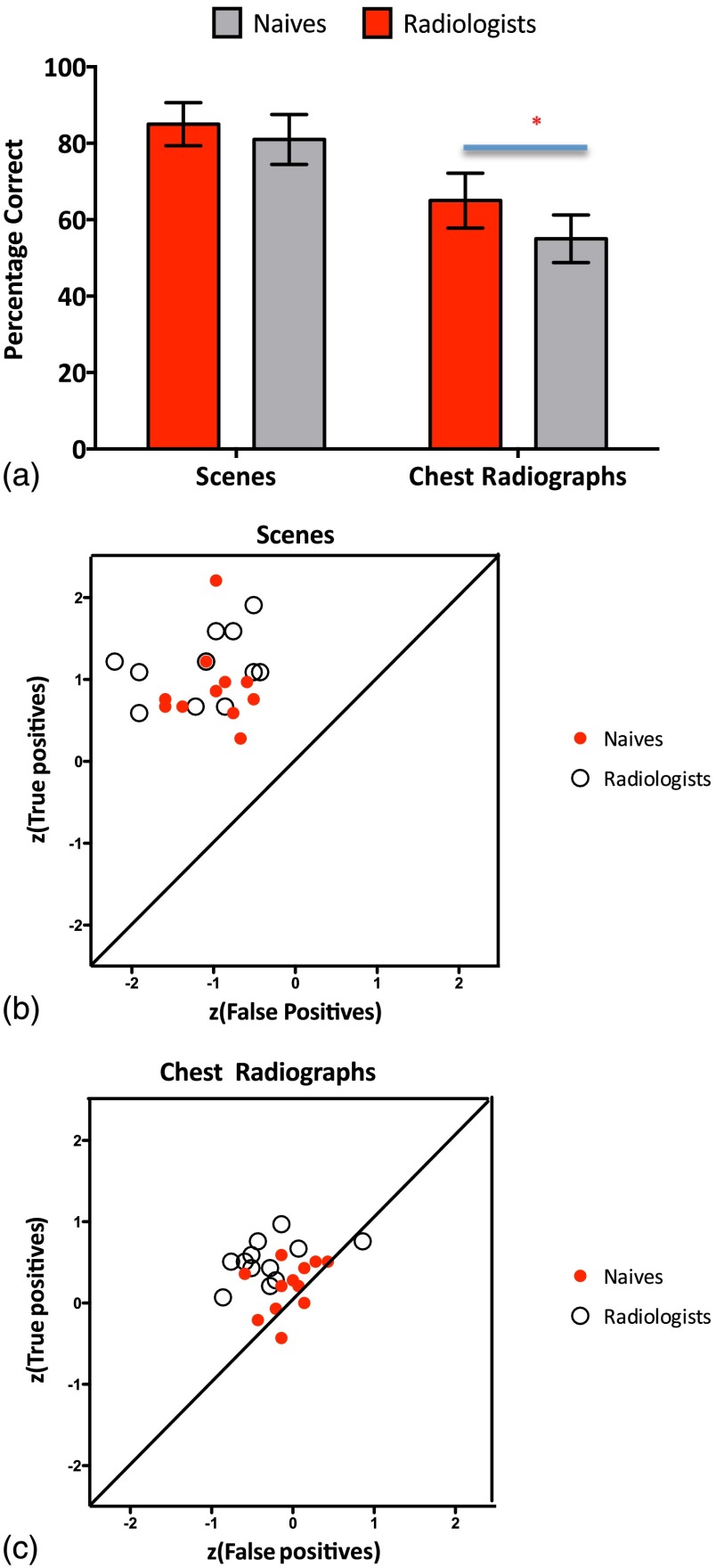
Fig. 2.
Performance on visual recognition memory test of the radiologists and medically naïve participants for two real scenes and chest radiographs. (a) Average accuracy for the two groups across two different image sets. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. An asterisk signifies a significant statistical difference. (b) Scatter plot of score true positives against score false positives by group for chest radiographs (radiologists’ average: 69% hits, 38% false positives; medically naïve average: 58% hits, 48% false positives). (c) Scatter plot of score true positives against score false positives by group for scenes (radiologists’ average: 86% hits, 17% false positives; medically naïve average: 80% hits, 17% false positives).