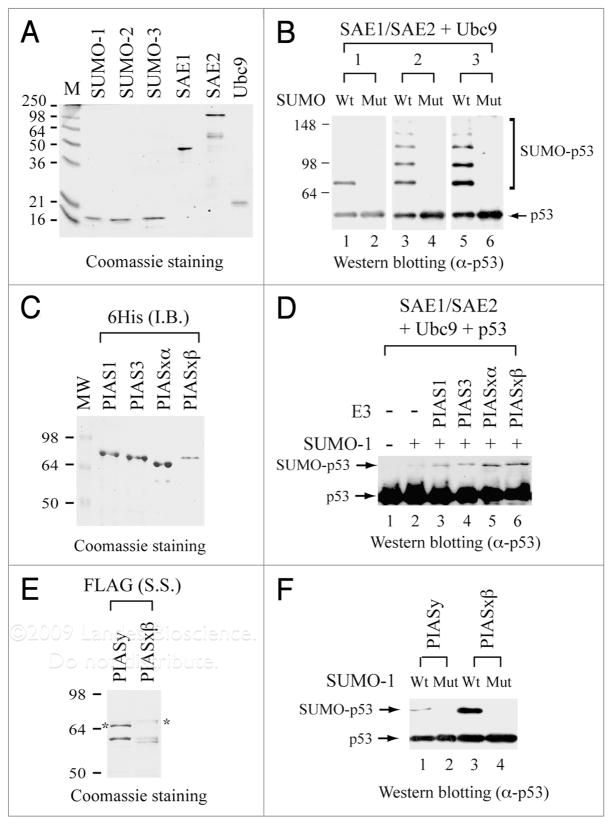
Figure 2.
In vitro reconstitution of p53 sumoylation with purified recombinant proteins. (A) Coomassie blue staining of purified human SUMO-1, SUMO-2, SUMO-3, SAE1, SAE2 and Ubc9. All these recombinant proteins are hexahistidine-tagged at their respective N-terminus and purified from bacteria as described.17 Prestained protein size markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. (B) Detection of sumoylated p53 (SUMO-p53) by immunoblotting. Sumoylation reactions were performed by incubating FLAG-tagged p53 with either wild-type (Wt) or the G-to-A mutant (Mut) of SUMO-1, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3, in the presence of E1 (SAE1/SAE2) and E2 (Ubc9) enzymes as described.17 Antibodies against full-length p53 (Santa Cruz) were used for detection by immunoblotting. (C) Coomassie blue staining of purified human PIAS1, PIAS3, PIASxα and PIASxβ. Each PIAS protein is hexahistidine-tagged at its N-terminus and purified from bacterial inclusion bodies (I.B.) as described.32 (D) PIAS enhances p53 sumoylation. Sumoylation and immunoblotting were performed as described in (B), in the absence (−) or presence (+) of a PIAS protein. (E) Coomassie blue staining of purified human PIASy and PIASxβ. Recombinant PIASy and PIASxβ, each FLAG-tagged at its N-terminus, were purified from bacterial sonication supernatant (S.S.) as described.33 Asterisk indicates the position of the full-length protein. The bands below the asterisk are degradation products from the full-length protein. (F) PIASy and PIASxβ purified from sonication supernatant also enhances p53 sumoylation. Sumoylation and immunoblotting were performed as described in (D) with the inclusion of PIASy or PIASxβ from (E).