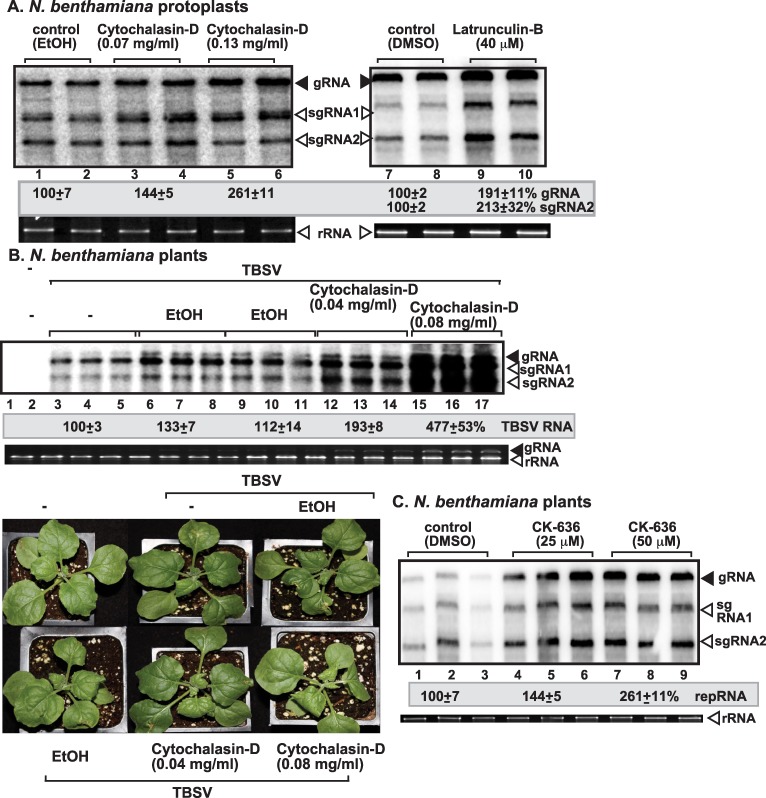
Fig 5. The effect of actin inhibitors on TBSV RNA accumulation in N. benthamiana protoplasts and plants.
(A) Northern blot analysis was used to detect genomic (g)TBSV RNA accumulation in protoplasts treated with Cytochalasin-D (lanes 3–6) and Latrunculin-B (lanes 9–10) to inhibit dynamic actin functions. Protoplasts from N. benthamiana were electroporated with TBSV gRNA and treated with various concentrations of the inhibitors as shown. Comparable concentrations of the solvents were used as controls. Total RNA samples were obtained 24 hours post-electroporation. The ethidium-bromide stained gel at the bottom shows ribosomal RNA as loading control. The two subgenomic RNAs made during the infection process are also detected. The accumulation level of TBSV RNA was normalized based on the rRNA. Each experiment was repeated three times. (B) The effect of actin inhibitor on TBSV RNA accumulation in N. benthamiana leaves. Northern blot analysis was used to detect gTBSV RNA. Treatment of N. benthamiana leaves with Cytochalasin-D promotes the accumulation of TBSV RNAs. Total RNA samples from the inoculated leaves were obtained 3 and 4 days post inoculation and used for Northern blotting (top panel) and gel analysis to show ribosomal RNA level. Symptom intensification caused by TBSV infection in plants treated with Cytochalasin-D. Note that leaf curling is more pronounced in TBSV-infected plants 3 days post-inoculation. (C) The effect of Arp2/Arp3 inhibitor on TBSV RNA accumulation in N. benthamiana leaves. Northern blot analysis shows gRNA and sgRNAs accumulation. See further details in panel B.