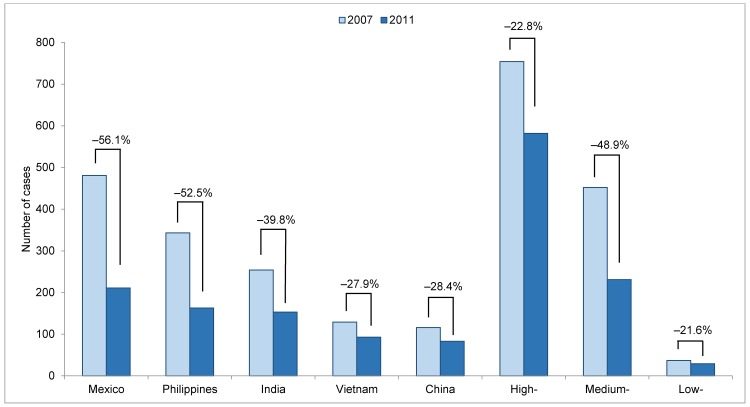
Fig 3. Tuberculosis case counts and percent decline among recent entrants, by country of origin or tuberculosis incidence in country of origin, 2007 and 2011.
Light shaded bars represent tuberculosis case counts in 2007, and dark shaded bars represent tuberculosis case counts in 2011. Percentages indicate the percent decline in case count for each group during 2007–2011. Recent entrants are foreign-born persons with <3 years since U.S. entry. The top five countries of origin accounting for the greatest number of tuberculosis cases among foreign-born persons in the United States are listed; cases among persons from other countries are classified according to tuberculosis incidence in the country of origin as low (<15 cases/100,000 persons), medium (15–99 cases/100,000 persons), or high (≥100 cases/100,000 persons). Countries with unknown incidence rates were excluded. All incidence rates used to categorize countries of origin are from World Health Organization data [1] and expressed per 100,000 persons.