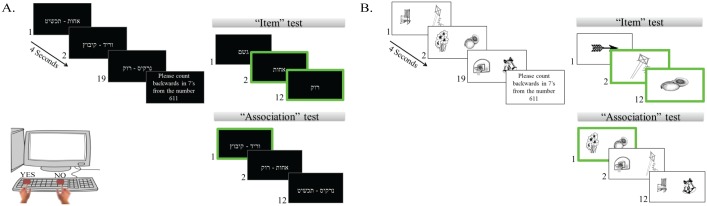
Fig 1. Experimental paradigm.
Participants performed two types of memory tasks (A. words, B. pictures) with a similar construct: a learning phase that was followed by two repetitions for items and associative memory recognition. Participants were presented with a study list of emotionally neutral pairs. In the item recognition task, participants had to identify the 6 items that appeared in the study list and reject the others. In the associative recognition task, participants had to identify the 6 correct pairs, which appeared in the study list and reject the new, recombined pairs. Highlighted green rectangles indicate targets.