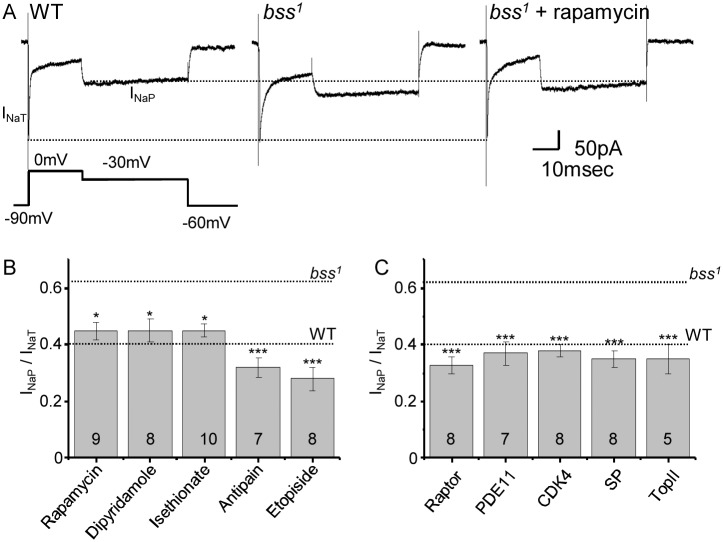
Fig 5. anticonvulsive compounds reduce INaP.
A) INaP is increased in bss1 relative to wildtype (WT). INaP was evoked using a voltage protocol that maintained the aCC neuronal membrane at 0mV to inactivate INaT before dropping to -30mV to measure maximal INaP. Treatment with rapamycin reduces INaP back to WT level. The three recordings shown were chosen because they have the same amplitude of INaT. The dotted lines are drawn as indictors only to show amplitudes of INaT and INaP in WT. B) Ratio for INaP/NaT recorded in aCC for bss1 raised in food containing either rapamycin, dipyramidole, isethionate, antipain or etopiside (concentrations as per Table 1). Values for untreated bss1 and WT are shown for reference. C) Ratio for INaP/NaT for bss1 following expression of RNAi transgenes targeting raptor, phosphodiesterase 11 (PDE11), CDK4, serine-type peptidase (SP) or topoisomerase II (TopII). Values are means ± sem.