Figure 1.
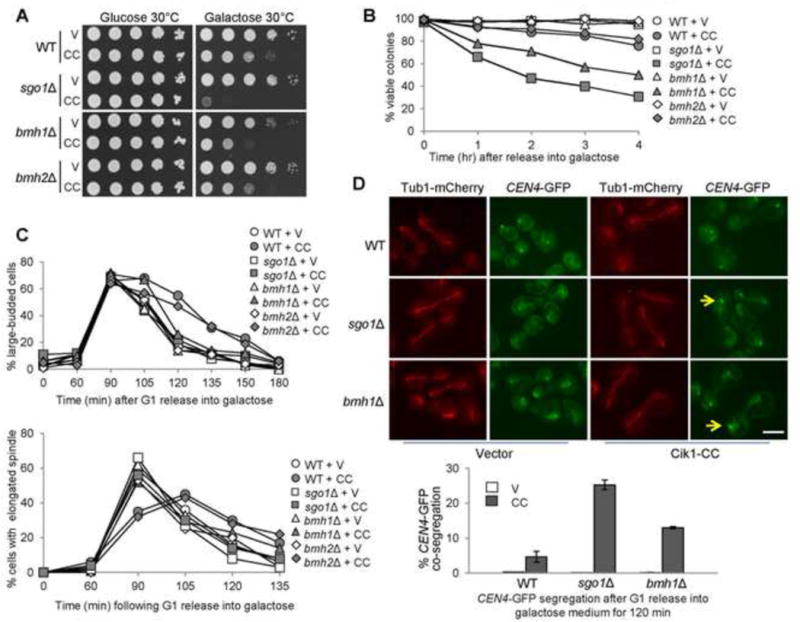
bmh1Δ cells are sensitive to CIK1-CC overexpression. (A) bmh1Δ cells overexpressing CIK1-CC show slow growth. Saturated cells with the indicated genotypes were 10-fold serial diluted, spotted onto glucose and galactose plates, and then incubated at 30°C for 2 days before scanning. V (vector), CC (PGALCIK1-CC). (B) bmh1Δ and sgo1Δ mutants, but not bmh2Δ, exhibit viability loss after CIK1-CC overexpression. Log-phase cells in raffinose were released into 2% galactose medium. Samples were taken and spread onto YPD plates to examine micro-colony formation after overnight incubation at 25°C (n > 300). (C) bmh1Δ and sgo1Δ but not bmh2Δ exhibit premature anaphase entry in the presence of tensionless attachments. PGALCIK1-CC plasmids were introduced to WT, bmh1Δ, sgo1Δ, and bmh2Δ cells with Tub1-mCherry. The transformants were synchronized in G1 phase in raffinose medium and using α factor and then released into galactose medium. Cells were collected and fixed to count the budding index and percentage of cells with elongated spindles (n > 100). (D) bmh1Δ and sgo1Δ cells overexpressing CIK1-CC show chromosome missegregation. PGALCIK1-CC plasmids were introduced to WT, bmh1Δ, and sgo1Δ cells with Tub1-mCherry and GFP-marked centromere of chromosome IV (CEN4-GFP). The transformants were synchronized in G1 in raffinose medium and then released into galactose-containing medium. After release for 120 min, the cells were fixed to examine the spindle morphology and CEN4-GFP segregation. Some representative cells are shown. Arrows indicate the cells with co-segregated CEN4-GFP. Scale bar = 5 μm. The percentage of cells with CEN4-GFP co-segregation was counted (n > 100). The result is the average of three repeats (bottom).
