Figure 4.
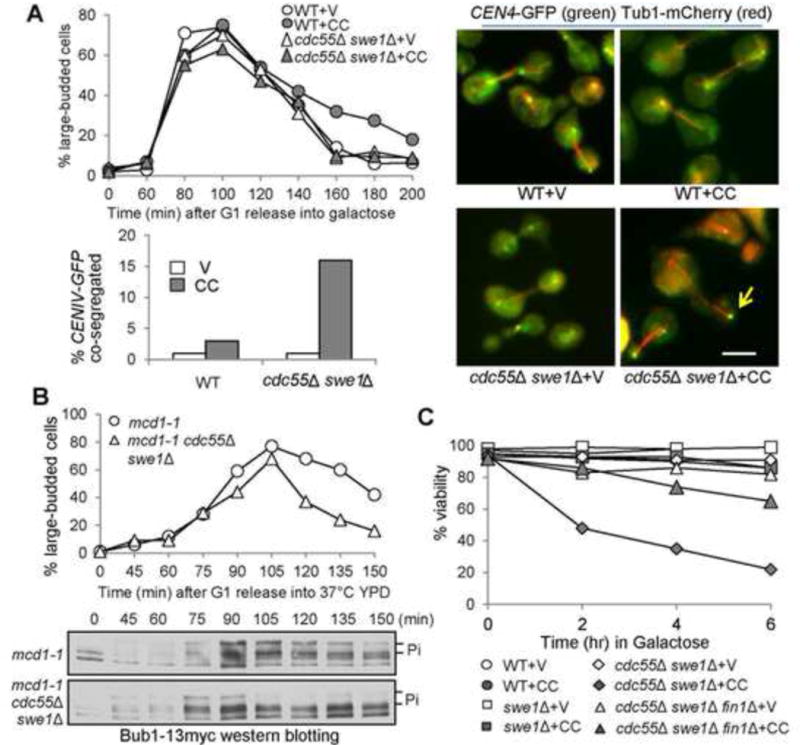
Cells with hyperactive FEAR are sensitive to syntelic attachment and show chromosome mis-segregation. (A) CIK1-CC overexpression causes chromosome mis-segregation in cdc55Δ swe1Δ cells. PGALCIK1-CC plasmids were introduced to WT and cdc55Δ swe1Δ cells with Tub1-mCherry and CEN4-GFP. The transformants were synchronized in G1 in raffinose medium and then released into galactose medium. After release for 120 min, the cells were fixed to examine the spindle morphology and CEN4-GFP segregation. The percentage of cells with CEN4-GFP co-segregation was counted (n > 100). Some representative cells are shown in the right panel. The arrow indicates a cell with co-segregated CEN4-GFP. Scale bar = 5 μm. (B) cdc55Δ swe1Δ cells exhibit premature Bub1 dephosphorylation in the presence of tensionless attachments. G1-arrested mcd1-1 and mcd1-1 cdc55Δ swe1Δ cells with Bub1-13myc were released into YPD at 37°C. Samples were collected periodically and subjected to western blotting. Here shows the budding index as well as the phosphorylation of Bub1. (C) The viability loss of cdc55Δ swe1Δ mutants induced by CIK1-CC overexpression is partially Fin1-dependent. Log-phase cells in raffinose were released into 2% galactose medium. Samples were taken every 2 hr and spread onto YPD plates. After incubation at 25°C overnight, the percentage of viable cells was counted (n > 300).
