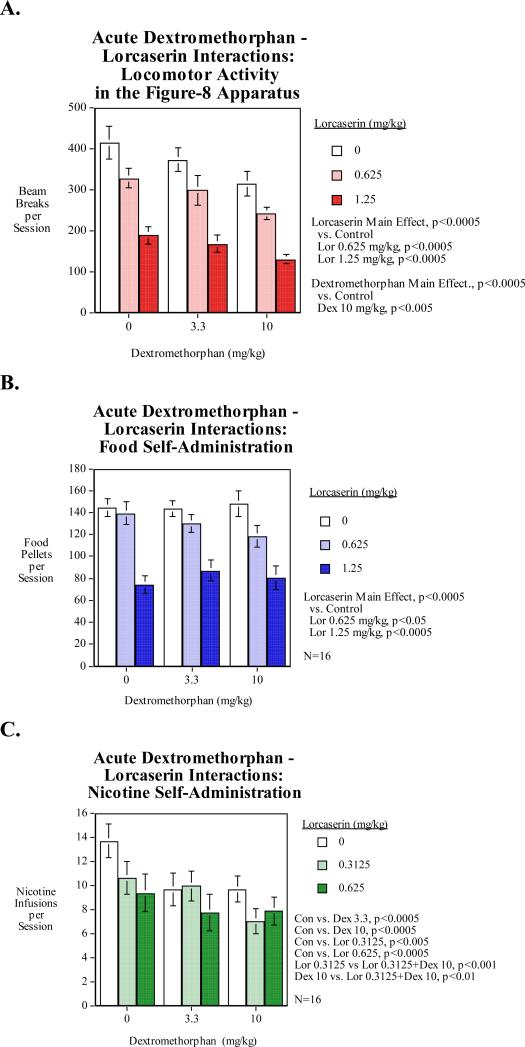
Figure 3. Dextromethorphan-Lorcaserin Interactions (N=16, mean±sem).
A) Locomotor activity: The dextromethorphan main effect was significant (p<0.0005) with the 10-mg/kg dose causing a significant (p<0.005) activitydecrease. The main effect of lorcaserin was also significant (p<0.0005) with both the 0.625-mg/kg and the 1.25-mg/kg doses causing significant decrease in locomotor activity.
B) Food motivated responding: The lorcaserin main effect was significant (p<0.0005) with the 0.625-mg/kg (p<0.05) and 1.25-mg/kg (p<0.0005) significantly decreased food motivated responding.
C) Nicotine self-administration: Both dextromethorphan doses significantly (p<0.0005) decreased nicotine self-administration. Both lorcaserin doses (0.3125-mg/kg p<0.005, 0.625 p<0.0005) also significantly reduced nicotine self-administration. The combination of 10-mg/kg of dextromethorphan and 0.3125-mg/kg of lorcaserin significantly reduced nicotine self-administration than 10-mg/kg dextromethorphan (p<0.01) or 0.3125-mg/kg lorcaserin (p<0.001) alone.