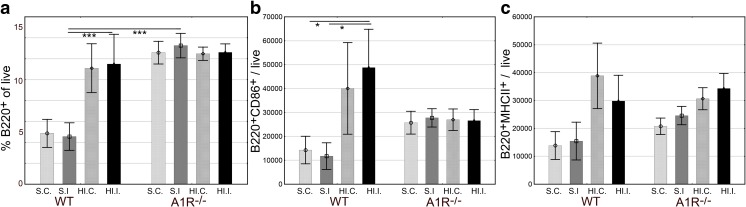
Fig. 3.
Differential B lymphocyte response to brain injury in A1R−/− mice 7 days after HI. S.C. sham contralateral hemisphere, S.I. sham ipsilateral hemisphere, HI.C. HI contralateral hemisphere, HI.I. HI ipsilateral hemisphere. a There was a robust B lymphocyte response in WT animals with increased percentage of live brain-infiltrating cells 1 week after HI. In A1R−/− mice, B lymphocytes failed to respond to the HI insult, although sham-operated animals had a significantly higher B lymphocyte infiltration than WT controls. b The number of CD86+ B lymphocytes increased after HI, however, only in the WT and not in the A1R−/−. c Antigen presenting function of B lymphocytes from A1R−/− mice appeared similar as the HI-induced change in MHC class II expression was comparable to WT (ANOVA p = 0.002 for treatment). Error bars indicate SE. A1R−/− sham-operated group n = 9, A1R−/− HI group n = 16, WT sham-operated group n = 6, WT HI group n = 3. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001