Figure 3. Spatial organisation of transcription activity in pituitary tissue.
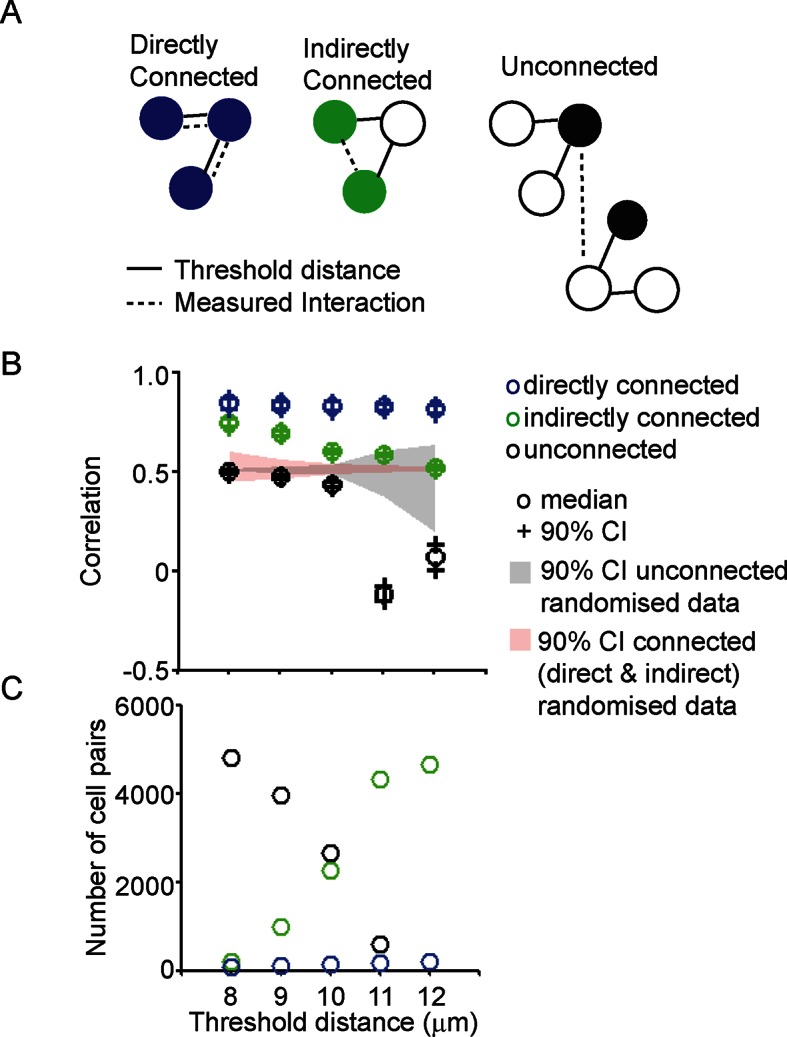
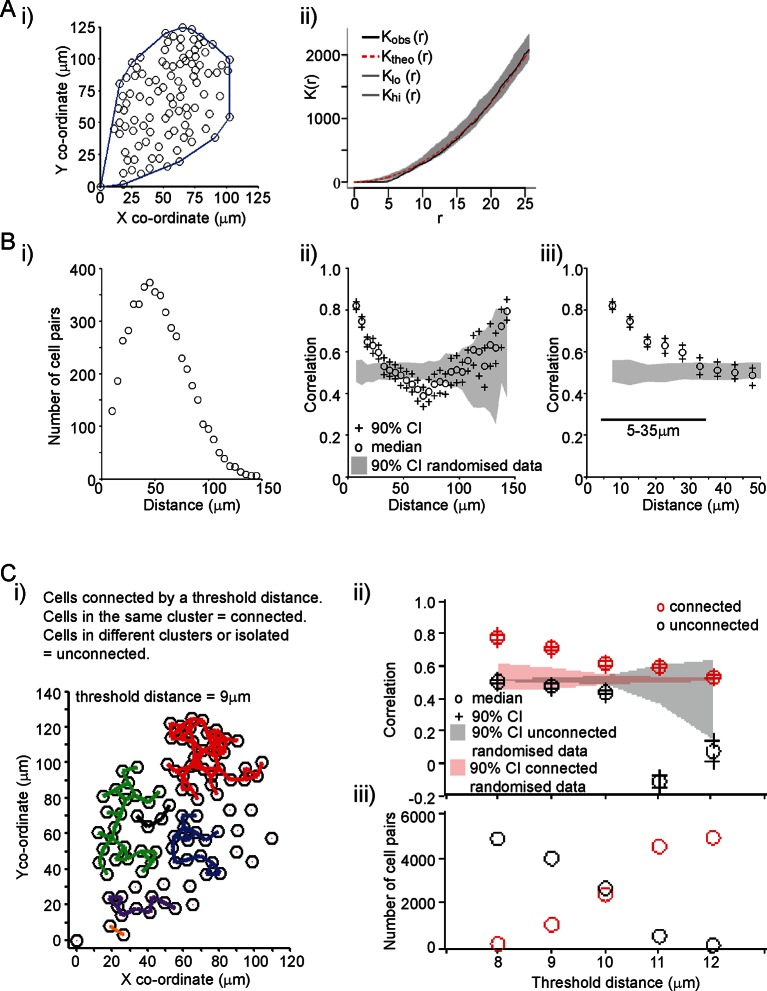
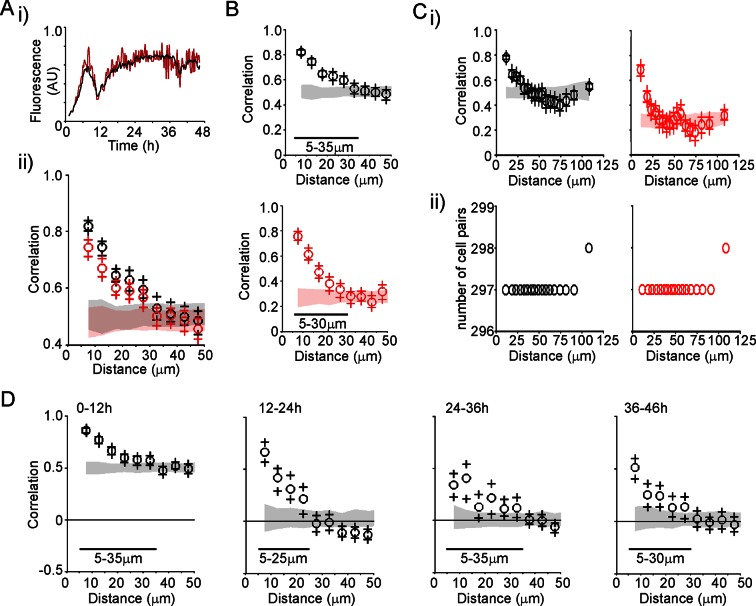
(A) Assessment of the spatial distribution of lactotroph cells with PRL gene transcriptional activity. i) The median position of the cells over the time-course along with the field or convex hull occupied by the cells. ii) Ripley’s k function was used to test whether the cellular distribution was random. The observed distribution (Kobs (r)) deviates from the theoretical prediction (Ktheo (r)) in the short r range due to the finite size of the cells, above which the cell distribution is found to be indistinguishable from random and within the 95% confidence interval (Klo (r) – Khi (r)). (B) Correlation vs distance analysis of cells from adult male pituitary tissue. The correlation between two time series xi and yi measured at N times is defined as . i) The distribution of distances between cell pairs. Correlation vs distance plots ii) all cell data and iii) cell pairs within 50 µm; indicate that proximally located cells have more similar activity than cells located further apart. The median and 90% confidence interval (CI) are shown along with the profile obtained from the 90% confidence interval of randomised of cellular transcription patterns. The range shown indicates the distances over which the randomised data were significantly greater (paired t-test, p<0.001) to the non-randomised data. (C) Analysis of correlation mediated by a potential lactotroph cell network in adult male pituitary tissue. i) Cell connectivity map with cells classified as connected or unconnected according to the threshold distance used. Connections between cells at a single time point are portrayed. ii) Correlation was calculated between connected (red) and unconnected cells (black) in parallel with randomised data. iii) The number of connected and unconnected cell pairs at various threshold distances. Connected cells were more correlated in their transcription activity than unconnected cells. Cell connectivity in ii)-iii) are based on median cell distances across the time-course to take into account cell movement. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments. PRL, prolactin.
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Characterisation of spatial organisation of prolactin transcription activity.
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Correlation of transcription profiles within a cellular network structure.