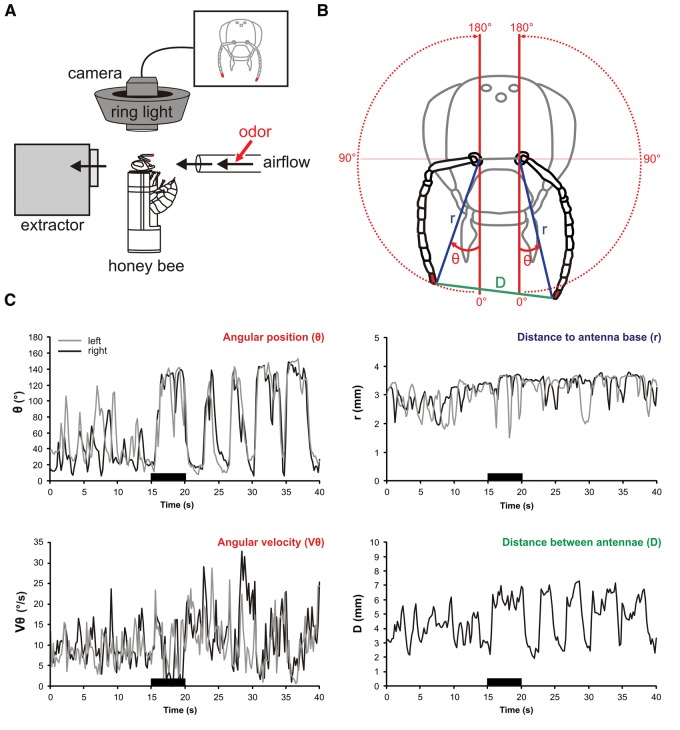
Figure 1.
Antennal movement recording. (A) Apparatus for recording antennal movements. Harnessed bees were placed in a dark room, under a cold light ring encircling a camera which recorded the coordinates of both antennal tips at a rate of 90 Hz. Olfactory stimulation was delivered to the bee from the front and an air extractor placed behind the animal prevented odorant accumulation. (B) Representation of the variables measured from antennal tip positions: (blue) distance to antenna base (r); (red) angular position (θ); (green) distance between both antennal tips (D). (C) Recordings taken before conditioning in response to 1-hexanol (black bar) for an individual bee. The same variables as in B are shown for this bee's two antennae (black line, right antenna; gray line, left antenna), with the addition of the angular velocity (Vθ) calculated from the angular position (θ).