Figure 5.
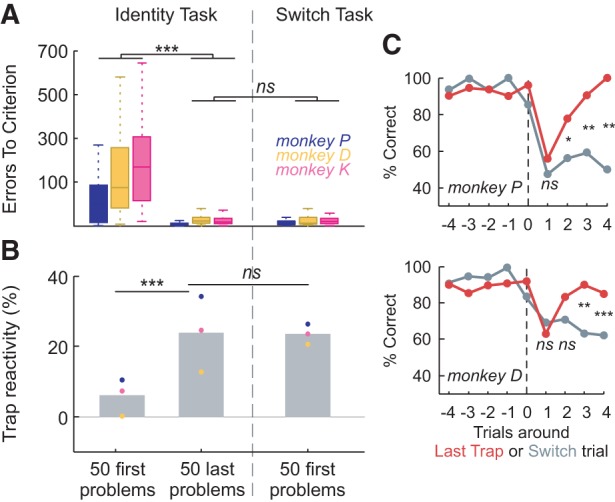
Switch task. (A) Excellent transfer from IT to the ST. Errors-to-criterion for the 50 first problems and the 50 last problems of the IT; and for the 50 first problems of the ST. (B) Trap reactivity is unchanged by task transfer, having increased during learning, suggesting that Trap reactivity acquired in IT is adaptive to ST. Gray bars represent averages of all monkeys. (C) Contrast of behaviors around Last Trap trials and Switch trials. Monkey P (top) shows performance that distinguishes the two forms of unexpected feedback from trial 2—the earliest possible moment. Monkey D's performance (bottom) distinguishes at trial 3. In this case only, the performance after Switch is calculated on the basis of the rules of the previous problem, to provide a comparable score between Switch and Trap. P-values compare the performance at LastTrap versus Switch. (*) P < 0.05; (**) P < 0.01; (***) P < 0.001; ns: nonsignificant.
