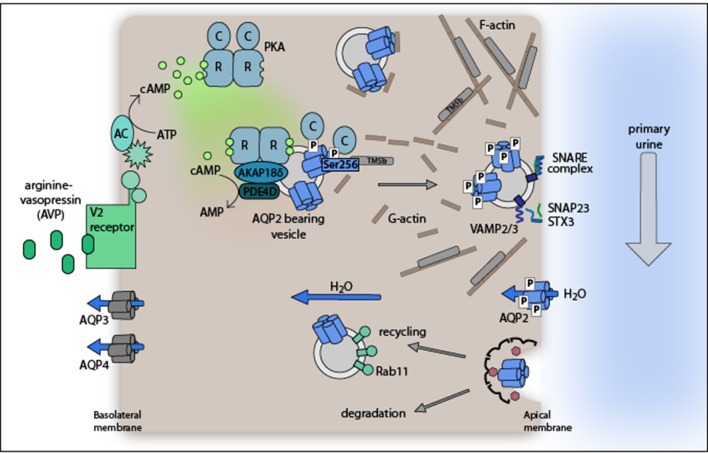
Figure 1.
Model of the arginine-vasopressin (AVP)-stimulated AQP2 translocation from intracellular vesicles into the plasma membrane of renal collecting duct principal cells. The plasma membrane insertion of AQP2 facilitates water reabsorption from hypoosmotic primary urine. The exocytosis-like process requires PKA phosphorylation of AQP2 at S256. Water exits the cells through water channels AQP3 and 4 constitutively expressed in the basolateral plasma membrane. For details please refer to section Proteins controlling AQP2 trafficking.