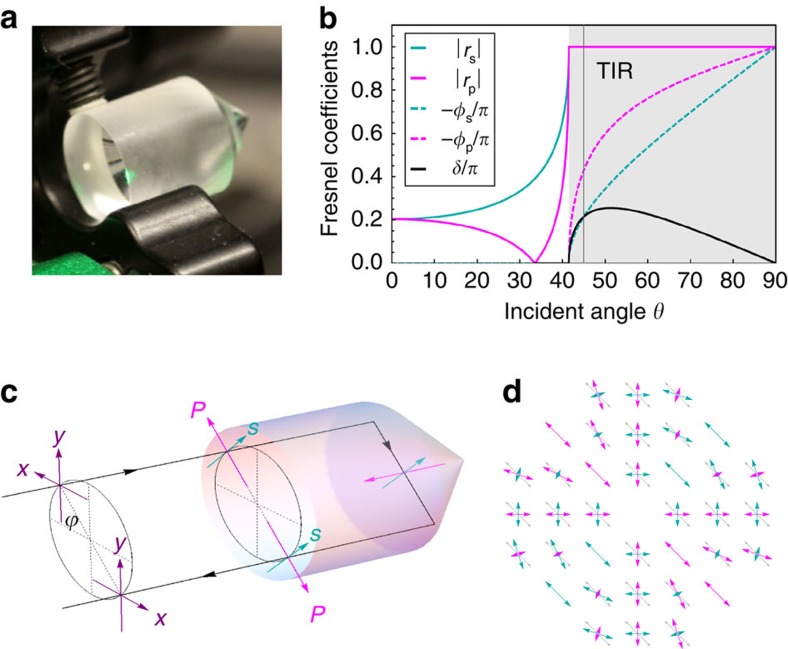
Figure 1. Total internal reflection from a solid glass cone.
(a) Photo of a solid glass cone. (b) Fresnel coefficients and phase shift (black line), assuming n=1.51. (c) Illustration of the axis conventions in the (x,y) and (p,s) bases. (d) Owing to the rotational cone symmetry, the decomposition of a linear polarized input beam (grey) into its s and p components (cyan and magenta, respectively) varies across the beam.