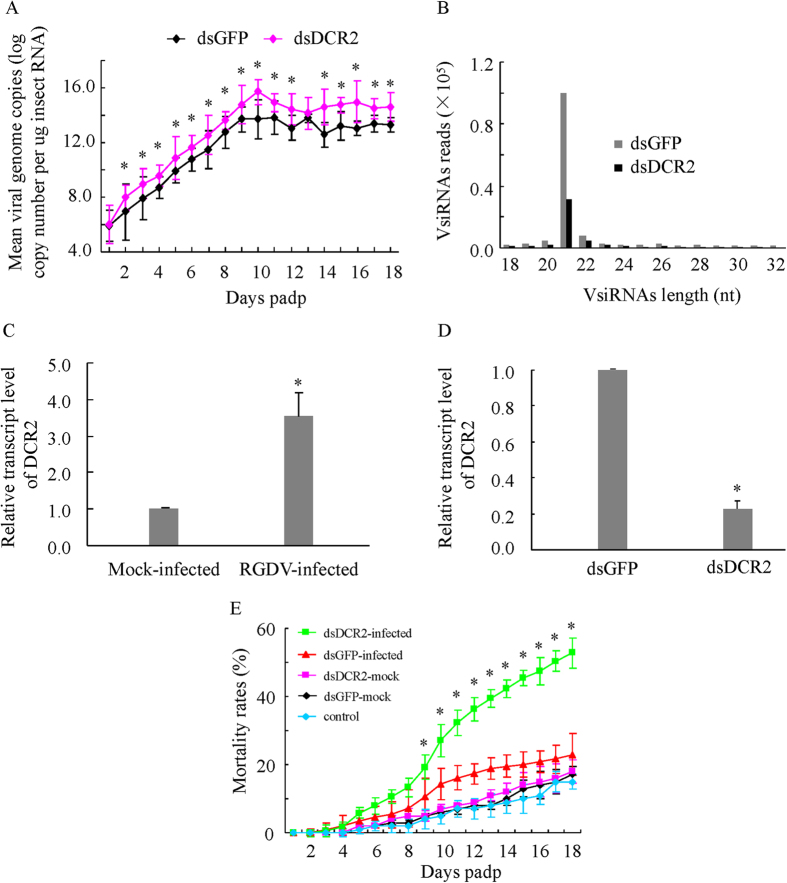
Figure 2. The siRNA pathway modulated the persistent infection of intact leafhoppers (R. dorsalis) by RGDV.
(A) Mean viral genome copies of dsDCR2- or dsGFP-treated viruliferous leafhoppers from 1 day to 18 days padp, as determined by RT-qPCR assay with mean ±SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (B) Abundance of vsiRNAs from dsDCR2- or dsGFP-treated viruliferous R. dorsalis at 9 days padp, as detected by small RNA deep sequencing. All reads in this analysis were redundant. (C) Relative transcript abundance of DCR2 gene in RGDV-infected or mock-infected R. dorsalis, as determined by RT-qPCR assay, with mean ± SD of three independent experiments *P < 0.05. (D) Relative transcript abundance of the DCR2 gene in dsDCR2- or dsGFP-treated R. dorsalis, as determined by RT-qPCR assay, with means ± SD of three independent experiments *P < 0.05. (E) Mortality of dsGFP- or dsDCR2-treated R. dorsalis which had fed on uninfected or infected rice plants or of nontreated R. dorsalis which had fed on uninfected rice plants. Mortality was monitored daily for 18 days padp. Means ± SD from three biological replicates are shown. *P < 0.05. Statistical analysis was conducted based on Tukey’s honest significant difference (HSD) test using SAS version IV (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).