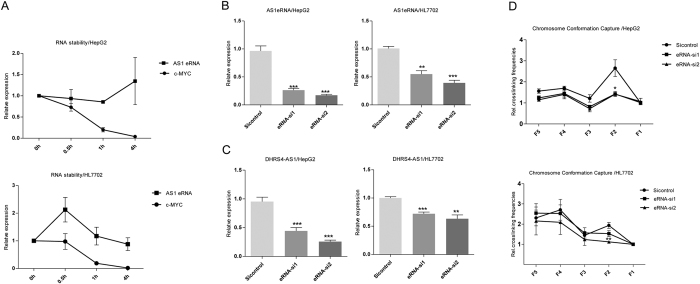
Figure 3. AS1eRNA enhances DHRS4-AS1 transcription by mediating DNA looping between the DHRS4-AS1 promoter and its enhancer.
(A) AS1eRNA is stable following treatment with actinomycin D. Cells were treated with 5 μg/ml actinomycin D, using c-MYC as the positive control in HepG2 and HL7702 cells. (B,C) After siAS1eRNA treatment, qPCR analysis of AS1eRNA and DHRS4-AS1 levels was performed at 48 h. The analysis of RNA levels used β-actin as the internal control. The siRNA-control was a scrambled sequence with no homology to any known gene. (D) The relative crosslinking frequencies of the AS1 enhancer/DHRS4-AS1 promoter were determined by qPCR. We first normalized the bias of the PCR efficiency among each primer set we used. This was performed by measuring the corresponding amplifications from a bacterial artificial chromosome, which was digested with HindIII and ligated with T4 DNA ligase. For correcting the differences of crosslinking and digestion efficiencies between samples, ERCC3 “control interaction frequencies” were used as internal control (see Methods). The relative crosslinking frequencies of F1~F5 was determined the fold change relative to the control region (F1). P values were determined by Student’s unpaired two-tailed t test. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.