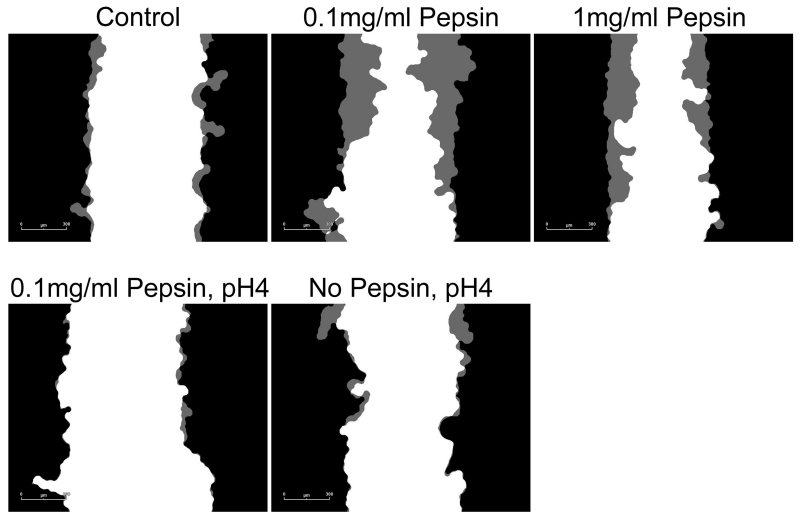
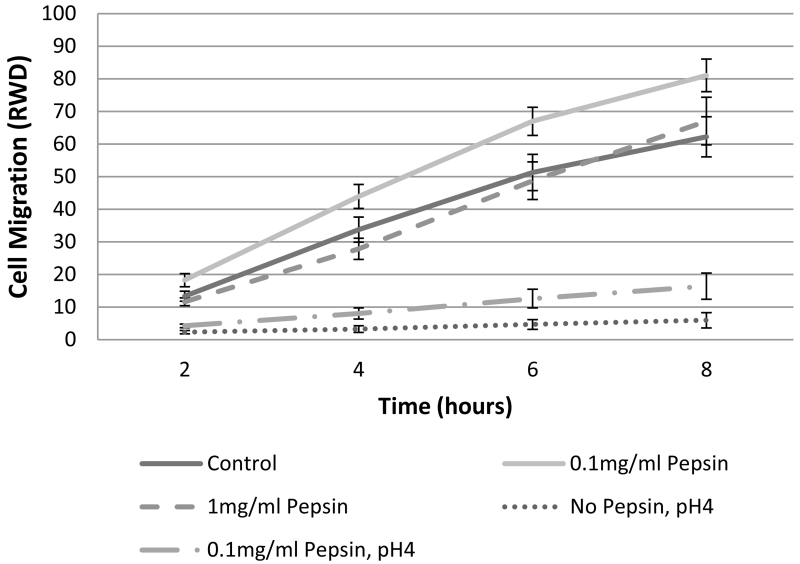
Figure 4. Esophageal cell migration in vitro is impeded by acid or acid/pepsin treatment, but enhanced by pepsin treatment.
Wound healing, or cell migration, was measured in confluent cultures of esophageal epithelial cells cultured from human biopsy via scratch assay. All pepsin alone (no acid) treatment conditions were initiated post-scratch and extended throughout the migration assay observation period; all pH4 treatments were limited to five minutes immediately prior to scratch because of the highly damaging nature of acid treatment. Cell migration into the area of the wound was monitored using an Essen Bioscience Live Cell Imaging System which provided (A) masks of the border of the initial wound (black) and cell migration progress (gray; 6 hours post-scratch shown, scale bar=300um), and (B) Relative Wound Density (RWD) as a metric of cell migration.