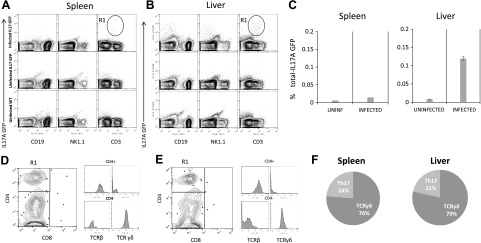
Figure 2.
IL-17A is mainly expressed by γδ and CD4+ T cells during L. donovani infection. A, B) IL-17A genetic expression reporter mice were infected with 1 × 107 L. donovani amastigotes. After 15 d of infection, spleen (A) and liver (B) were obtained, and the expression of IL-17A was investigated among immune subsets of B cells (CD19+), NK cells (NK1.1+), and T cells (CD3+). Uninfected IL-17A GFP mice and uninfected WT mice were used as controls to determine IL-17A-positive cells. C) Frequencies of IL-17A GFP+ cells were analyzed in total splenocytes or nonparenchymal liver cells. D, E) CD3+ IL17A+ cells were gated in A and B as R1 and CD4 and CD8 expression was analyzed by flow cytometry in the spleen (D) or liver (E). Histograms represent the expression of TCRβ or TCRγδ in CD4+ or CD4-/low subsets gated in the dot plot, showing that CD4+ cells expressed TCRβ, whereas CD4−/low expressed TCRγδ. F) Frequency of T cells expressing IL-17A based on their phenotypic characterization by flow cytometry. Data represent 3 independent experiments (n = 3).