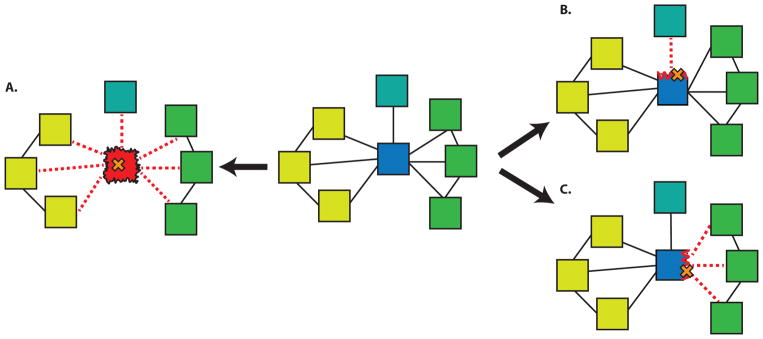
Figure 4.
Various mechanisms of SNP-induced disruption in protein-protein interaction networks. A SNP that destabilizes a hub protein can ablate all associated interactions (A). SNPs disrupting different interfaces of the hub may interfere with interactions active in different tissues (B, C). Blue (hub protein), Yellow (nodes expressed in tissue1), Green (nodes expressed in tissue2), Turquoise (node expressed in tissue3). Mutation in cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) leads to metabolic disease called Homocystinuria. Among many HGMD SNPs impacting this protein, experimental evidence [63] suggest that I278T mutation leads to destabilization of CBS, which further disrupts of all three important interactions involving this protein and this is equivalent to removing a node from the PPI network. Mutation in EFHC1 gene, which has been implicated in epilepsy, presents a good example of edgetic effect [43]. This mutation perturbs interaction of EFHC1 with ZBED1 and TCF4. While the perturbed interaction between EFHC1 and ZBED1 interfere with cell proliferation [64], on the other hand disturbance in EFHC1 and TCF4 interaction influence the neuronal differentiation process [65].