Figure 2.
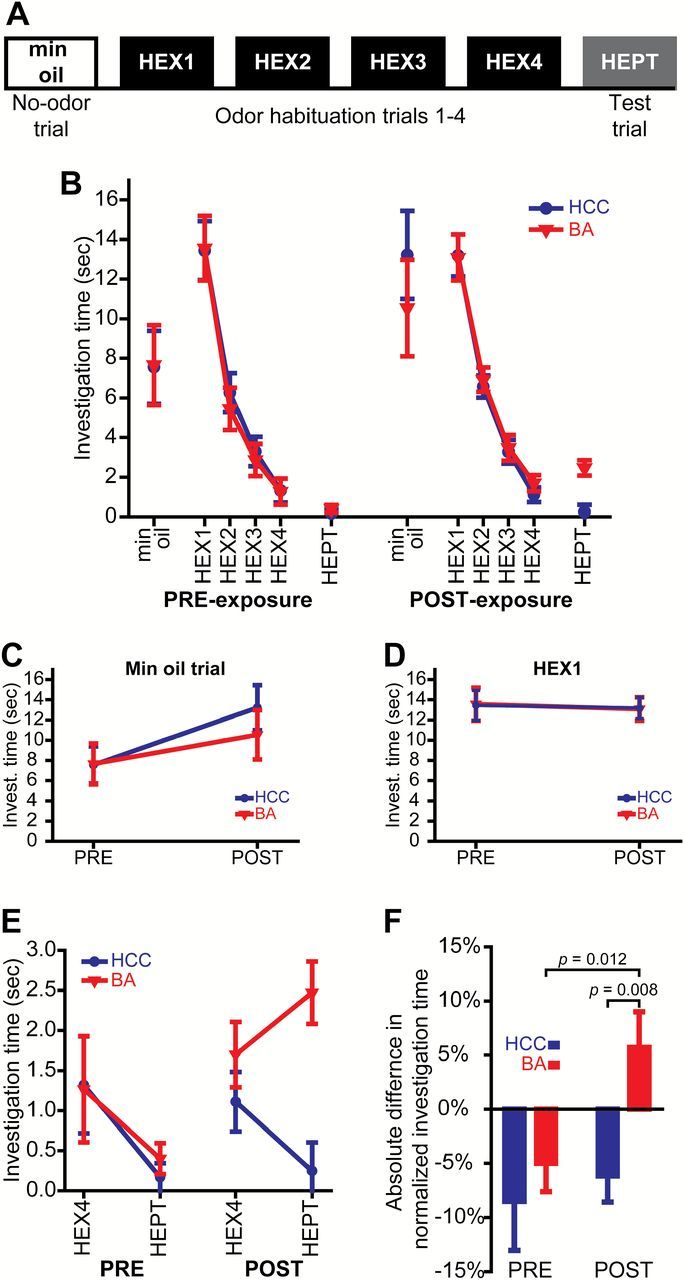
Chronic odorant exposure enhances olfactory discrimination abilities, but does not alter general motor activity or the propensity to investigate an odor object. (A) Procedure summary for the habituation/dishabituation testing protocol. (B) Summary of all data from PRE- and POST-exposure testing sessions. Investigation time during the mineral oil (no odor) trial (C) and the first habituation trial (HEX1) (D) before (PRE) and after (POST) the 7-day exposure period. (E) Investigation time during the last habituation trial (HEX4) and the test trial (HEPT) before and after HCC or BA exposure. (F) Difference scores (normed HEPT minus normed HEX4) for both groups during both behavioral test sessions. The data in B–F are shown as group means ± SEMs, and P values are by between-groups or paired t-tests.
