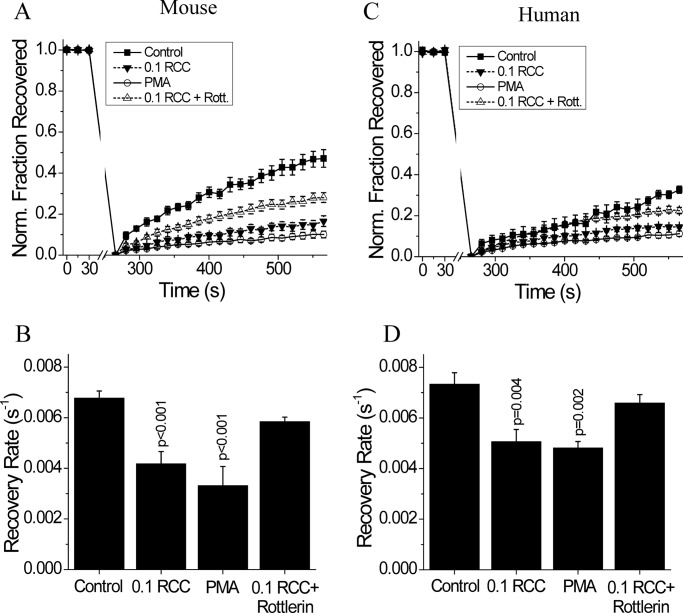
FIGURE 5.
PKCδ dependence of cytokine-mediated disruption of gap junctions in mouse and human islets. A, average fraction of fluorescence recovered over time, normalized to the average fluorescence before photobleaching; and B, gap junction coupling, as measured by fluorescence recovery rate during FRAP, in mouse islets treated with 0.1 RCC, with 300 nm of the PKCδ activator PMA, or with 0.1 RCC plus 1 μm of the PKCδ inhibitor rottlerin, each for 1 h. Data are averaged over islets from n = 6 or 7 mice. C, fraction of fluorescence recovered over time, normalized to the average fluorescence before photobleaching; and D, gap junction coupling in human islets treated with 0.1 RCC and/or PKCδ modulators, as in A. Data are averaged over islets from n = 5 or 6 batches of islets from separate donors. Error bars on all panels represent S.E. p values indicate significant differences compared with untreated controls (analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc analysis, α = 0.05).