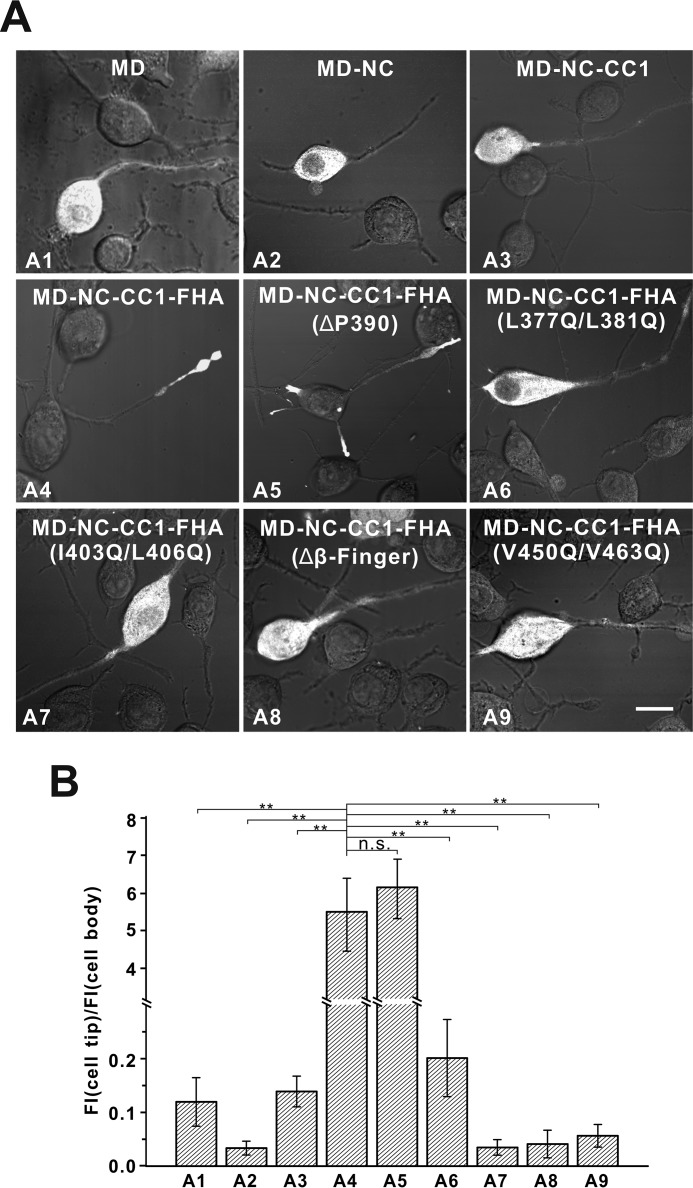
FIGURE 9.
The NC-CC1-FHA tandem is essential for motor activation. A, cellular localizations of the MD, MD-NC, MD-NC-CC1, and MD-NC-CC1-FHA fragments and various MD-NC-CC1-FHA mutants. The MD, MD-NC, and MD-NC-CC1 fragments were all enriched in the cell body (A1–A3), whereas the MD-NC-CC1-FHA fragment was predominantly localized to the cell periphery (A4). The MD-NC-CC1-FHA mutants with the mutations to disrupt the dimer were localized in the cell body (A6–A9), but the NC-CC1-FHA(ΔPro-390) mutant was localized to the cell periphery (A5). Scale bar: 20 μm. B, quantification of the cellular distribution data shown in panel A. The ratio of the tip to cell body average fluorescence intensity (FI) was quantified for each construct for more than 15 cells (n > 15). Each bar represents the mean value ± S.D. **, p < 0.05. n.s., not significant.