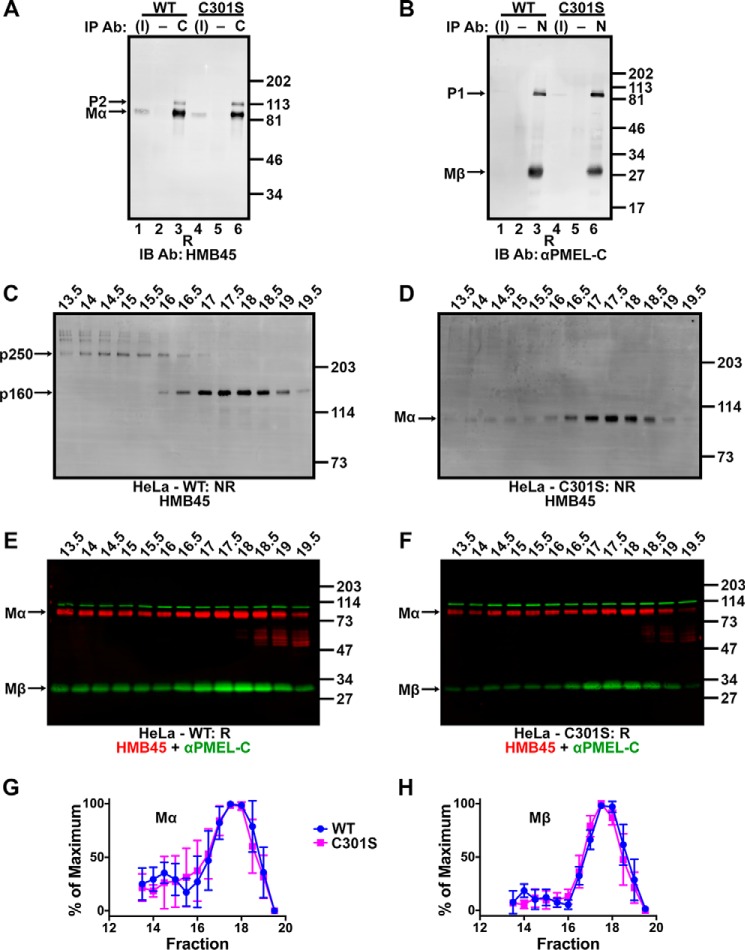
FIGURE 10.
Non-covalent complexes with properties similar to p250 and p160 persist despite Cys-301 mutagenesis. A and B, detergent-soluble lysates prepared from transiently transfected HeLa cells expressing wild-type PMEL (lanes 1–3) or PMEL C301S (lanes 4–6) were immunoprecipitated (IP) using αPMEL-C to the Mβ fragment (C; lanes 3 and 6 in A), NKI-beteb to the Mα fragment (N; lanes 3 and 6 in B) or matched negative (−) controls (normal rabbit serum in A, lanes 2 and 5, or the irrelevant monoclonal antibody OKT4 in B, lanes 2 and 5). The immunoprecipitated material and 3% of the inputs (I; lanes 1 and 4) were analyzed by reducing SDS-PAGE (R) and immunoblotted (IB) with antibodies to the opposite fragment: HMB45 to Mα (A) or αPMEL-C to Mβ (B). The migration of molecular weight standards are shown to the right; bands corresponding to P2, Mα, P1, and Mβ are indicated with arrows. C–F, HeLa cells transfected with wild-type PMEL (C and E) or the C301S PMEL variant (D and F) were lysed in 250 mm n-octylglucoside lysis buffer and the detergent extract fractionated by size exclusion chromatography in 25 mm n-octylglucoside running buffer. Eluted fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing (NR; C and D) or reducing (R; E and F) conditions and immunoblotted using the antibodies indicated. The migration of molecular weight standards is indicated to the right of each blot, and bands corresponding to p250, p160, Mα, and Mβ are indicated by arrows. Lanes are labeled with fraction numbers as presented in Fig. 3A. G and H, HMB45 and αPMEL-C immunoreactivity was quantified to determine the amount of Mα (G) and Mβ (H) present in each fraction. The lowest value quantified for each species was set to 0%, and the highest value was set to 100% for each experiment. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments.