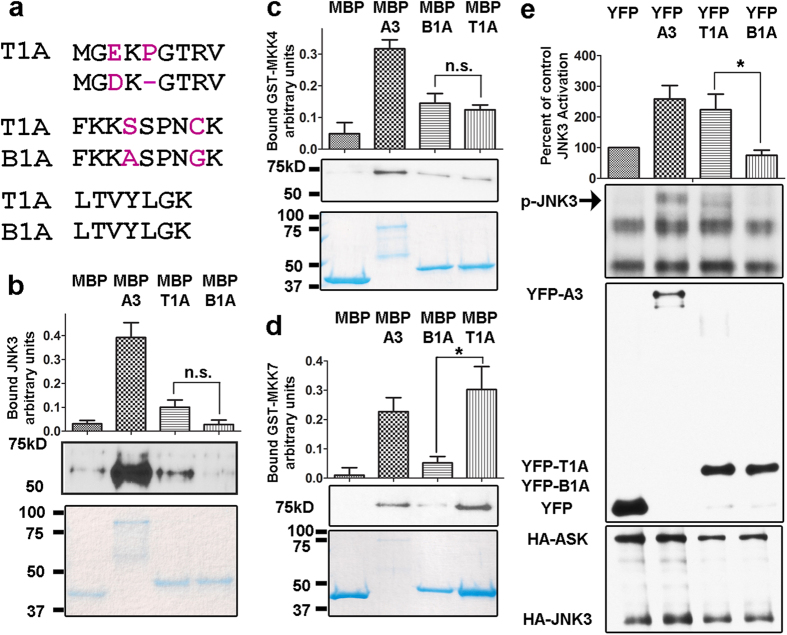
Figure 5. T1A activity is specific.
(a) Sequence comparison of arrestin-3-derived T1A and B1A, derived from arestin-2, which does not facilitate JNK3 activation . Residues that differ between T1A and B1A are shown in magenta. (b–d) Pull-down of purified JNK3 (b), MKK4 (c), and MKK7 (d) by MBP (negative control), MBP-arrestin-3 (positive control), MBP-T1A, and MBP-B1A, was performed, as described in Methods. Lower panels, Coomassie gels of loaded MBP-fusions; middle panels, Western blots of retained JNK3 (b), MKK4 (c), and MKK7 (d); upper panels, quantification of Western blots from 3-4 independent experiments. Note that B1A binds MKK4 like T1A, but does not appreciably interact with JNK3 or MKK7. (e) COS7 cells co-expressed HA-ASK1 and HA-JNK3α2 with YFP (negative control), YFP-arrestin-3 (Arr3, positive control), YFP-T1A, or YFP-B1A. Lower two blots show expression levels of indicated proteins; upper blot and bar graph (quanitification of JNK3α2 phosphorylation in four independent experiments) show that T1A facilitates JNK3α2 phosphorylation, whereas B1A does not. *p < 0.05; n.s., not significant. Full blots and gels are shown in Supplemental Fig. S5.