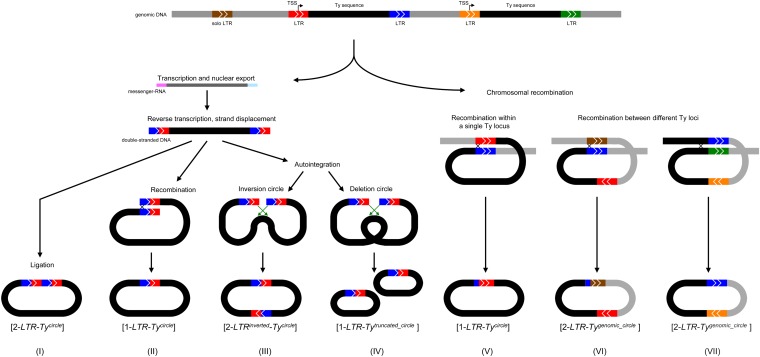
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the different paths to Ty eccDNA formation. For scenarios I–IV (see Figure 1), sequence reads covering the LTR regions from eccDNAs will all display an apparent breakpoint at the site corresponding to the transcription start site (TSS, top panel). Ligation (scenario I) mediated by nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) of 3′- and 5′-LTR ends (Kilzer et al. 2003). Recombination of LTRs (scenario II) mediated by homologous recombination (Farnet and Haseltine 1991). Auto-integration (scenarios III and IV) caused by double-stranded Ty DNA insertion into its own sequence rather than into the nuclear genome (indicated by green arrows) (Garfinkel et al. 2006). For scenarios V, VI and VII (Farahbaugh and Fink 1980; Jordan and McDonald 1999a; Libuda and Winston 2006; Møller et al. 2015), intrachromatid recombination and crossover events is envisioned at any position along the entire length of the LTR sequences of Ty eccDNAs.