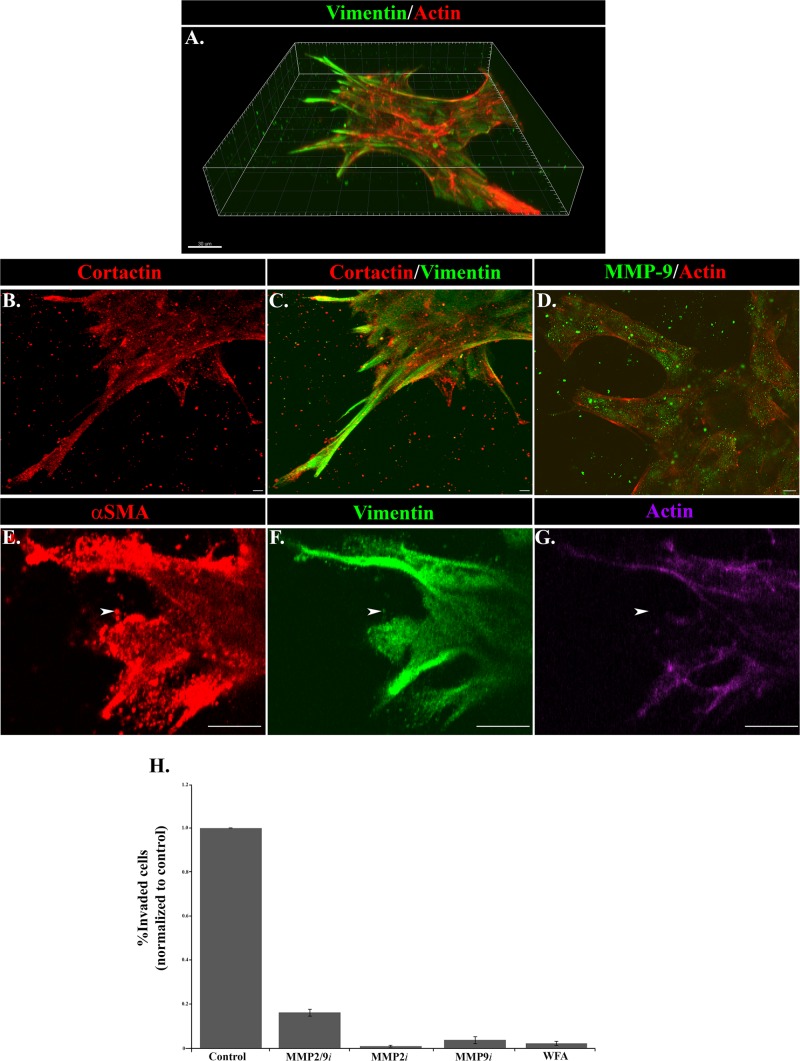
FIGURE 7:
Functional properties of invading cells in response to injury. (A–G) The 3D Matrigel invasion assay of ex vivo–wounded explants at (A–D) day 6 in culture and (E–G) day 2 in culture. (A) A 3D reconstruction of a confocal Z-stack of cords of cells in the injury invasion assay labeled for vimentin (green) and F-actin (red), emphasizing the extension of vimentin-rich cells into the Matrigel matrix in leader-cell positions. Bar, 30 μm. (B, C) Cords of invading cells in the Matrigel invasion assay were immunolabeled for cortactin (red) and vimentin (green) and viewed by confocal microscopy. This projection image of a confocal Z-stack shows that the processes extended by the vimentin-rich mesenchymal cells into the Matrigel also expressed cortactin (red). Bar, 5 μm. (D) Labeling for MMP-9 (green) in cells at the leading edges of the cords extended into Matrigel and was distributed in discrete vesicular structures in the cells (F-actin; red) and also in a punctate pattern just beyond the cells in the Matrigel matrix, where it can act to degrade the matrix for invasion. A representative single optical plane captured by confocal microscopy. Bar, 10 μm. (E–G) Vimentin-rich cells at the invading front (green) also express αSMA (red), often with a punctate distribution (arrowhead). Labeling for F-actin (purple) was mostly absent from the areas with a strong distribution of αSMA puncta, suggesting that this actin population was nonfilamentous. A representative single optical plane captured by confocal microscopy. Bar, 10 μm. (H) The individual roles of MMP-2/9 and vimentin in invasion after wounding were evaluated using an inhibitor approach in the Matrigel-Transwell chemoinvasion assay. This study included the MMP-2 inhibitor MMP-2i, the MMP-9 inhibitor MMP-9i, the combined MMP-2/9 inhibitor MMP-2/9i, and the vimentin inhibitor WFA. Invaded cells from at least 10 capsules were counted and quantified using MetaMorph or NIS Elements image analysis software. Relative numbers of invaded cells were plotted on graphs ±SEM. MMP-2 and MMP-9 function were required for invasion of cells in the Matrigel-Transwell assay. MMP-2 inhibited invasion by 99%, MMP-9 by 96%, and MMP2/9 by 84% in the Matrigel-Transwell assays. Inhibiting vimentin function with WFA suppressed invasion in the Matrigel-Transwell assay by 98%.