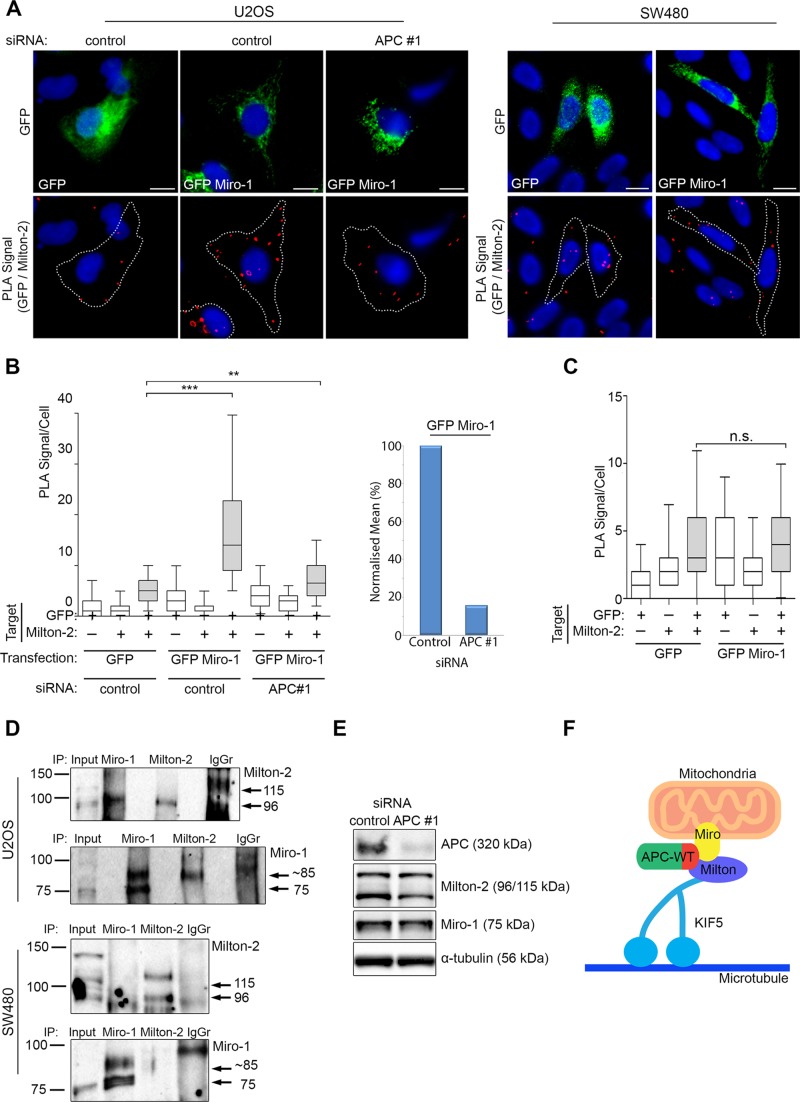
FIGURE 9:
Full-length APC promotes assembly of the Miro-1/Milton-2 complex. (A) U2OS cells (treated with control siRNA or APC #1 siRNA) and SW480 cells expressing GFP alone or GFP-Miro-1 were subjected to Duolink PLA and analyzed for their ability to form protein complexes with endogenous Milton-2. Representative images from immunofluorescence microscopy are shown with PLA-positive protein complexes indicated by red dots. Scale bars: 10 μm. (B) The PLA signals per cell were scored in U2OS to reveal that the number of complexes formed between GFP Miro-1 and endogenous Milton-2 was significantly reduced following loss of APC (left panel). This was also presented as mean PLA signal/cell after subtraction of GFP background (right panel). (C) In SW480 cells, no significant interaction above background level was detected. Statistical significances are indicated on the graphs (***, p < 0.001; **, p <0.05; n.s., not significant). Box-and-whisker plots are presented as a median (line), upper/lower quartile (box), and min/max (error bars with 95% CI). Statistical analysis by Mann-Whitney U-test, with Bonferroni correction applied to (B). (D) U2OS and SW480 cells were subjected to IP assays using antibodies to pull down Miro and Milton. In U2OS cells, Milton was successfully detected in Miro pull downs and vice versa. In SW480 cells, however, Milton/Miro complexes were not detected by IP. (E) Total-cell extracts from U2OS cells treated with control siRNA or APC #1 siRNA were analyzed by Western blot to detect APC, Milton-2, Miro-1, and α-tubulin (loading control). No change in protein expression level was detected between the two samples. n > 100 cells for each sample from more than two independent experiments. (F) A proposed summary model is shown to indicate that APC has a role in initiation of anterograde mitochondrial transport through a C-terminal (indicated in red) interaction with the Miro/Milton complex. Note that the illustration is conceptual and that specific details of protein–protein interactions and the role of potential additional binding partners are not yet known.