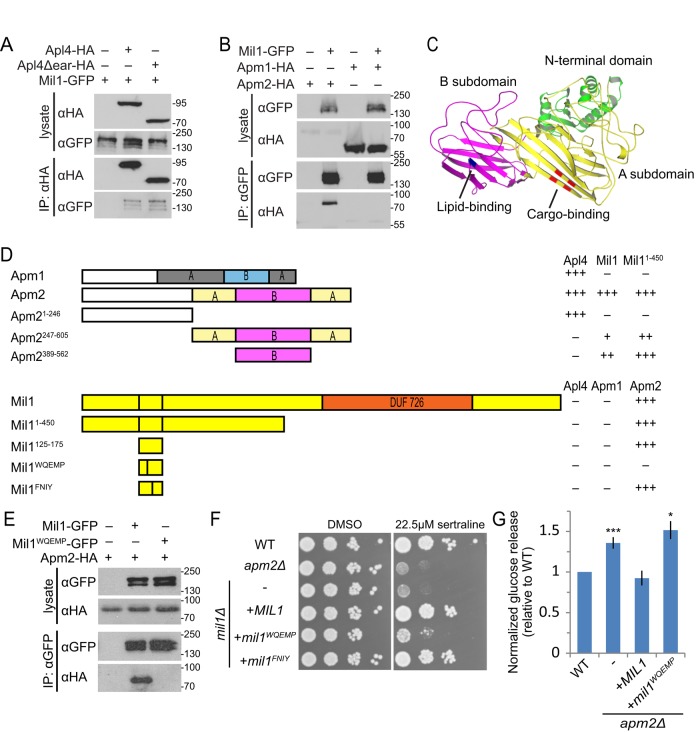
FIGURE 4:
Mil1 interacts with Apm2 through its WQEMP motif. (A) Mil1-GFP copurified with immunoprecipitated Apl4-3HA and with a truncated version lacking the γ appendage (Apl4Δear-HA) known to bind several AP-regulatory proteins. Loading of lysate relative to immunoprecipitate was 1:9. All proteins were genomically tagged. (B) Pull down of Mil1-GFP in strains coexpressing either Apm1-3HA or Apm2-3HA shows that Mil1 binds specifically to Apm2. All proteins were genomically tagged. (C) Phyre2 homology model of Apm2, colored to indicate the N-terminal AP-binding domain (green) and a C-terminal region composed of A (yellow) and B (magenta) subdomains. Key residues predicted to be involved in YxxΦ binding (red) or lipid binding (blue) based on alignment with regions of AP-1 and AP-2 μ subunits are indicated. (D) Yeast two-hybrid mapping of Apm2-Mil1–binding domains. Full-length or truncated Apm2 constructs were fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GBD), and full-length, truncated, or mutated Mil1 constructs were fused to the GAL4-activating domain (GAD). Qualitative interaction strengths are indicated. Mil1WQEMP represents the W143QEMP>AAEAA mutant, and Mil1FNIY represents the F152NIY>ANAA mutant. (E) Anti-GFP immunoprecipitation of plasmid-expressed wild-type Mil1-GFP or Mil1WQEMP-GFP from strains coexpressing genomically tagged Apm2-3HA. (F) Sertraline sensitivity was assessed by plating strains in a 10× dilution series on YPD containing 22.5 μM sertraline or DMSO as a control. (G) The mil1WQEMP mutant is unable to restore sorting of the Snc1 reporter GSS. Cell-surface GSS levels in the indicated strains were determined by quantifying invertase activity and normalizing to levels in wild-type cells. Unpaired t test compared with wild type, ***p < 0.0001 and *p < 0.05. Error bars represent SEM (n = 10).