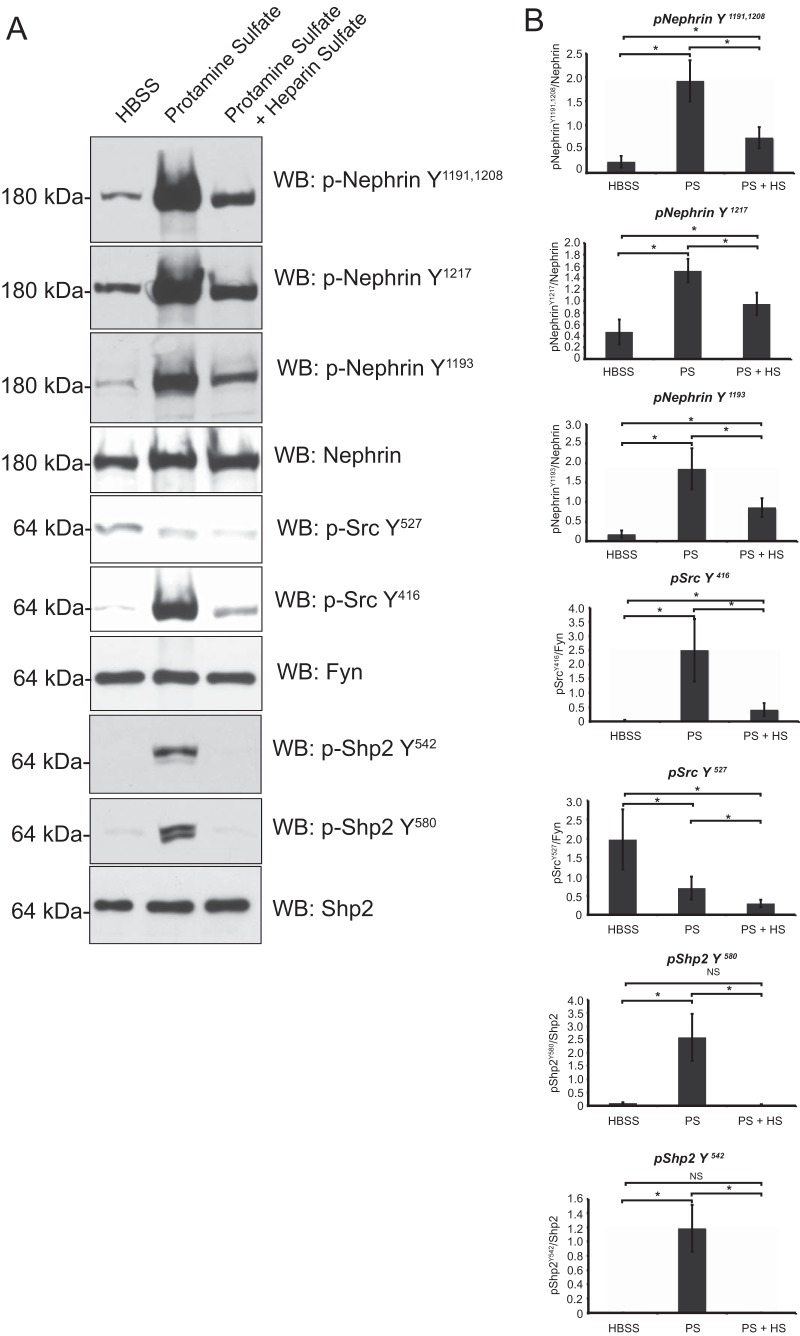
FIG 5.
Phosphoproteome analysis of isolated glomerular detergent-resistant membrane fractions following protamine sulfate injury. (A) Glomeruli were isolated from mouse kidneys perfused with HBSS, protamine sulfate, and protamine sulfate followed by heparin sulfate. The glomerular lysates were fractionated using the flotation gradient method to obtain the DRMs. Following resolution of lysates using SDS-PAGE, the membranes were blotted with the indicated antibodies. The blots are representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Quantification of nephrin, Shp2, and Src phosphorylation using densitometry. Glomeruli from mouse kidneys perfused with HBSS, protamine sulfate (PS), and protamine sulfate followed by heparin sulfate (PS + HS) were isolated and fractioned using a flotation gradient. Detergent-resistant membrane fractions were resolved using SDS-PAGE and blotted for the indicated antibodies (Fig. 4). ImageJ software was used to quantify the bands from three different experiments. There was an increase in nephrin tyrosine phosphorylation using three different antibodies against residues necessary for nephrin-Nck interaction. There was an increase in Shp2 activation, suggested by an increase in tyrosine phosphorylation of Shp2 Y542 and Y580 following protamine sulfate perfusion. There was an increase in Src tyrosine phosphorylation on the Y416 residue and a decrease in tyrosine phosphorylation of the Src Y527 residue following protamine sulfate perfusion. Heparin sulfate reversed the phosphorylation on nephrin, Shp2, and Src Y416. Src Y527 dephosphorylation persisted following heparin sulfate perfusion. The data are mean values ± standard errors of the mean. *, P < 0.001; NS, not significant using a two-tailed t test.