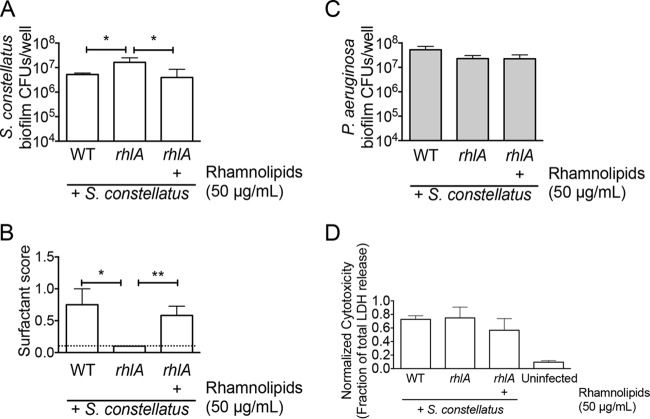
FIG 6.
Exogeneous rhamnolipids reduce S. constellatus viability in biofilms on CF airway cells. (A and B) Shown are the viability (A) and surfactant scores (B) of S. constellatus 7155 grown as single and mixed biofilms on CF airway cells with the wild type or the rhlA mutant of P. aeruginosa treated with 50 μg/ml rhamnolipids, as indicated. The dashed line indicates the limit of detection. (C) Viability of the wild type or the rhlA mutant P. aeruginosa grown as mixed biofilms on CF airway cells with S. constellatus 7155 treated with 50 μg/ml rhamnolipids, as indicated. (D) Cytotoxicity of indicated mixed biofilms on CF airway cells. Cytotoxicity was normalized to total cell lysis. For all panels, the bars and error bars indicate the means and SD of the results from three biological replicates. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, as determined by an unpaired t test.