FIG 4.
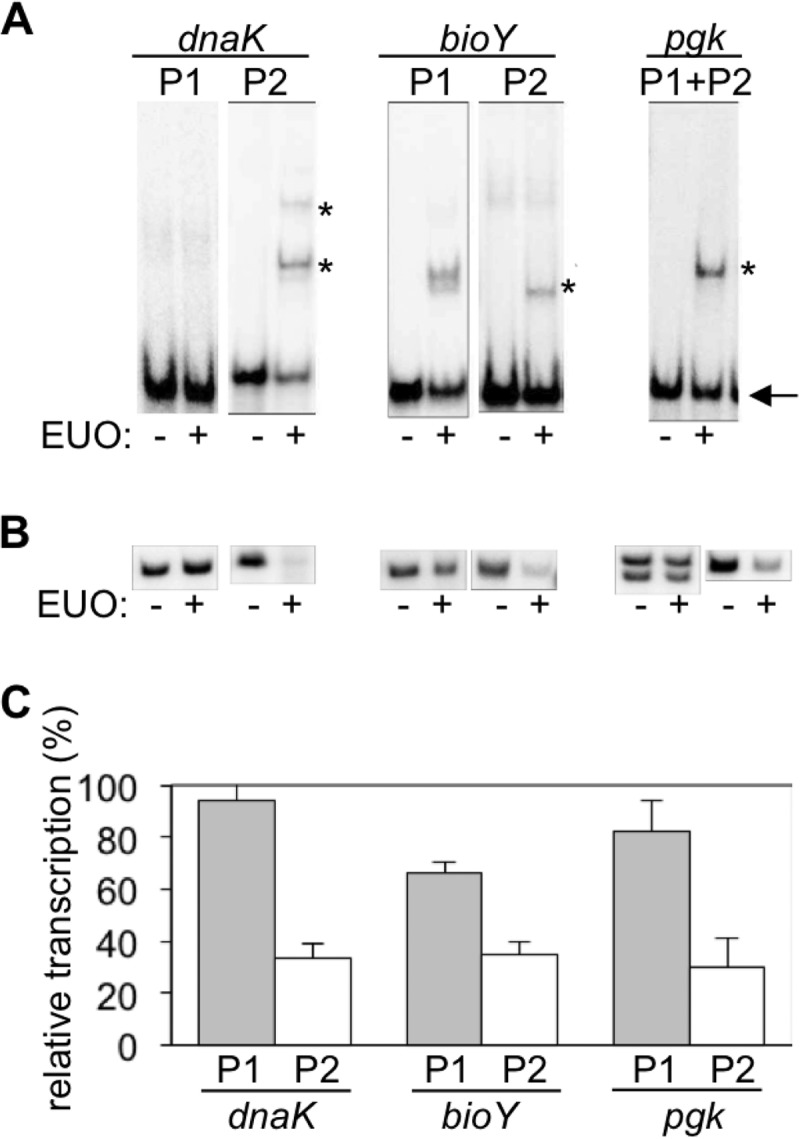
Promoter-specific binding and repression by the late regulator EUO. (A) EMSAs with the P1 (σ66) or P2 (σ28) promoter regions of dnaK, bioY, and pgk, performed in the absence or presence of 160 nM rEUO. Each promoter was present on a 60-bp DNA probe. Bands corresponding to the bound probes are represented by an asterisk, and the free probe is indicated with an arrow. (B) Representative in vitro transcription assays measuring the effect of EUO on these six promoters. The σ66-dependent promoters were transcribed by E. coli σ70 RNA polymerase, and the σ28-dependent promoters were transcribed with σ28 RNA polymerase reconstituted from E. coli core enzyme and recombinant C. trachomatis σ28. Each assay was performed in the absence or presence of 2.5 μM rEUO. (C) Graph showing the effect of EUO on the transcriptional activity of each promoter. For each promoter, transcription in the presence of EUO is reported as a percentage of the baseline level of transcription in the absence of EUO. Values are averages from at least 3 independent experiments with standard deviations (indicated by error bars).
