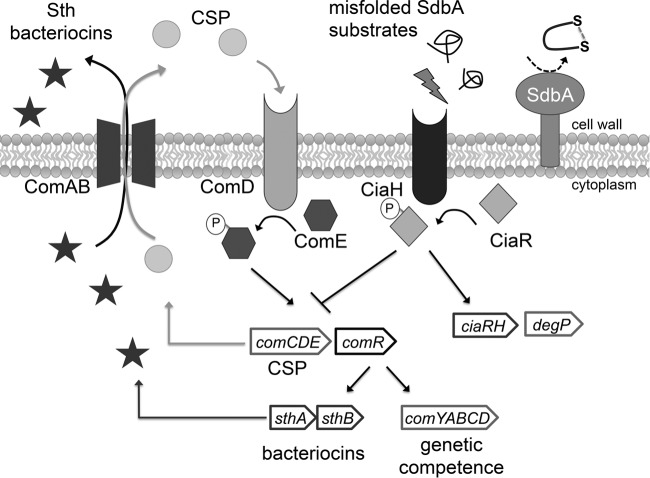
FIG 6.
Summary of the pathway regulating bacteriocin production in S. gordonii. Bacteriocin production in S. gordonii is regulated by the Com quorum-sensing system, which also controls genetic competence. The system is activated by extracellular competence-stimulating peptide (CSP), which is encoded by comC. When ComD, a histidine kinase located at the cell surface, binds to CSP, it becomes active to phosphorylate its cognate response regulator, ComE. ComE drives the expression of the comCDE operon in an autoregulatory loop, as well as the ComAB transporter required for CSP and bacteriocin secretion. In addition to ComE, the Com pathway requires two alternative sigma factors, ComR1 and ComR2, to activate expression of the genes required for genetic competence (comYABCD), as well as the sthA and sthB bacteriocins. Mutation of the disulfide oxidoreductase SdbA generates a signal that results in upregulation of the CiaRH two-component regulatory system. Activation of CiaRH somehow shuts down the Com system, leading to loss of bacteriocin production.