FIG 1.
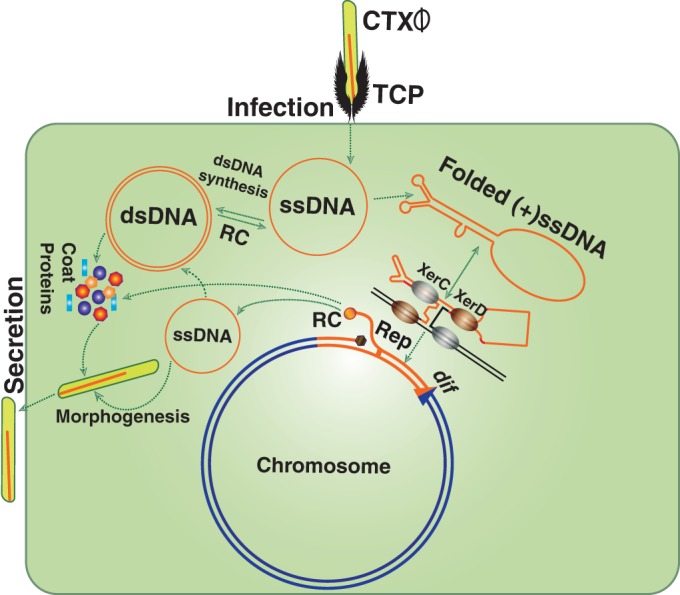
Diagram showing key steps in the life cycle of CTXϕ. The phage recognizes a V. cholerae cell by sensing the presence of cell surface receptor using the toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP). CTXϕ delivers its ssDNA genome into the host cytoplasm, where it is either converted into a replicative double-stranded phage genome (pCTXϕ) or directly integrated into dif1/dif2 by exploiting two host-encoded tyrosine recombinases, XerC and XerD. Productions of virions from the prophage genome relies on rolling-circle (RC) replication.
