FIG 6.
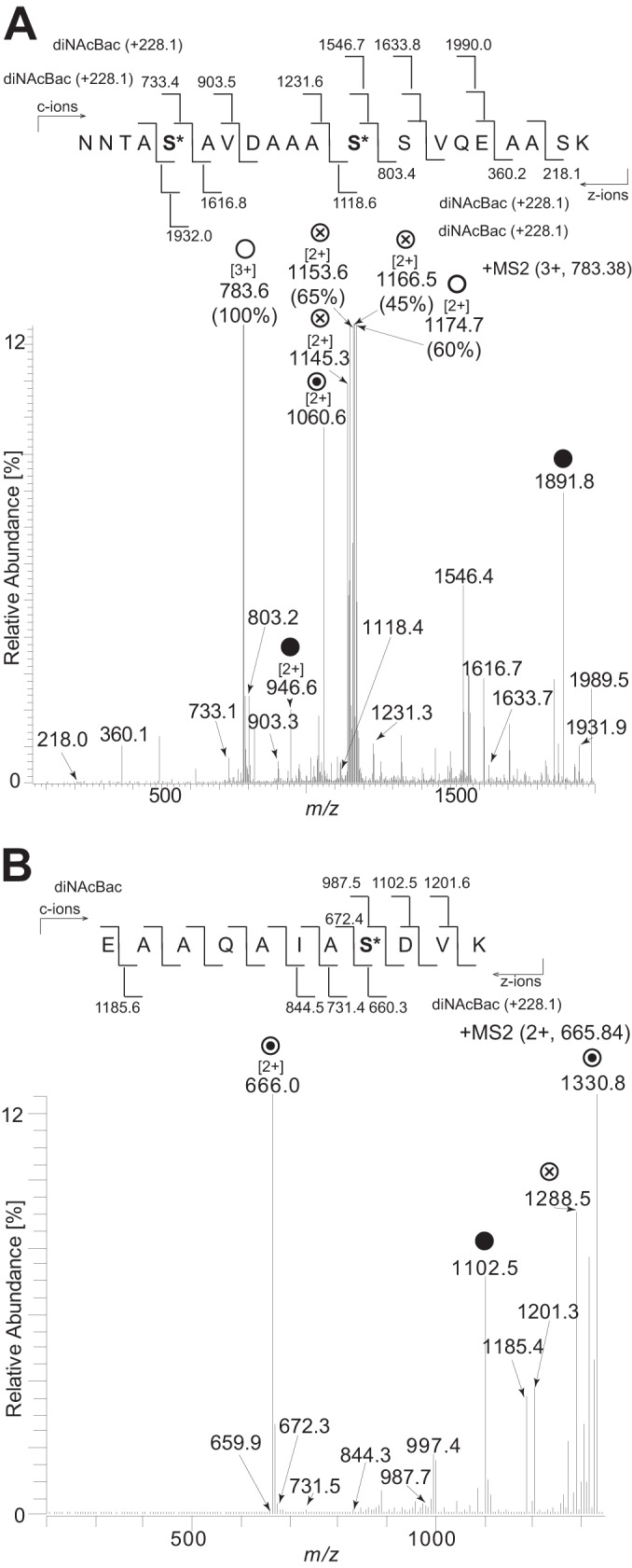
Identification of serines as glycan occupancy sites by ETD analysis. (A) Fragmentation of the triply charged peptide at m/z 783.38 corresponding to the peptide 38NNTASAVDAAASSVQEAASK57 carrying two diNAcBac modifications at serine 42 and serine 49. (B) Fragmentation of the doubly charged peptide at m/z 665.84 corresponding to the peptide 27EAAQAIASDVK37 carrying a diNAcBac modification at serine 34. ○ denotes ions corresponding to the full-length peptide with two diNAcBac modifications. ⊗ denotes ions generated by internal glycan fragmentation. ⊙ denotes ions corresponding to the full-length peptide with a single diNAcBac modification. ● denotes the mass of the full-length unmodified peptide. Bracketed numbers denote the charge state of the ion if different from 1. Numbers in parentheses denote the full relative intensity of the ion. The strain used was the cycC-His pglH strain (KS951).
