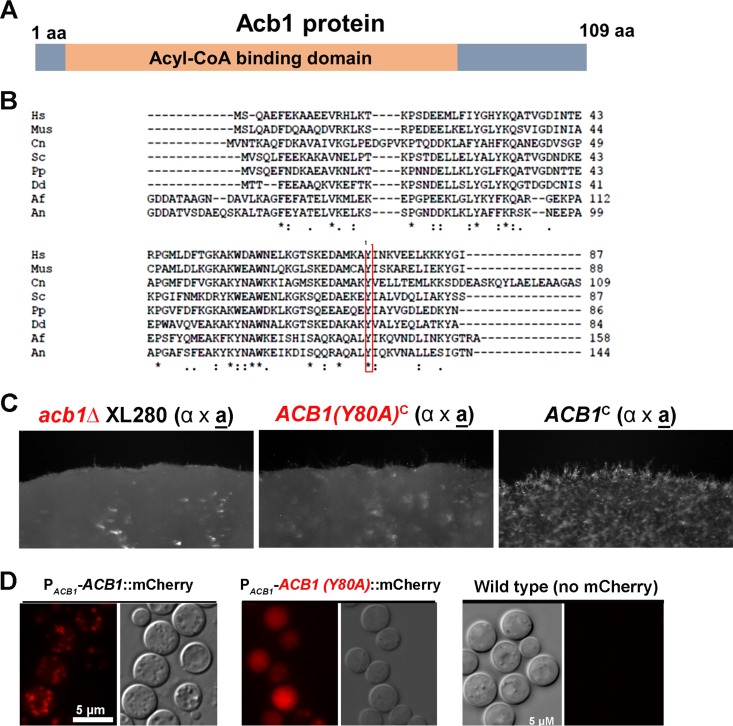
FIG 4.
Mutation of the key residue Y80 affects the function and subcellular localization of Acb1. (A) Diagram of the Acb1 protein. (B) Acb1 is a highly conserved protein among different species. Shown is a multiple alignment of proteins from the following species: Hs, Homo sapiens; Mus, mouse species; Cn, Cryptococcus neoformans; Sc, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Pp, Pichia pastoris; Dd, Dictyostelium discoideum; Af, Aspergillus fumigatus; An, Aspergillus nidulans. (C) The mutated Acb1(Y80A) strain could not restore the filamentation defect of the acb1Δ mutant. The acb1Δ mutant, the acb1Δ mutant transformed with the wild-type allele [ACB1c], and the acb1Δ mutant transformed with the Y80A allele [ACB1(Y80A)c] were cultured on YNB medium for 48 h. (D) Subcellular localization of Acb1-mCherry and Acb1(Y80A)-mCherry. The fluorescent image of nontransformed wild-type cells was used as the negative control.