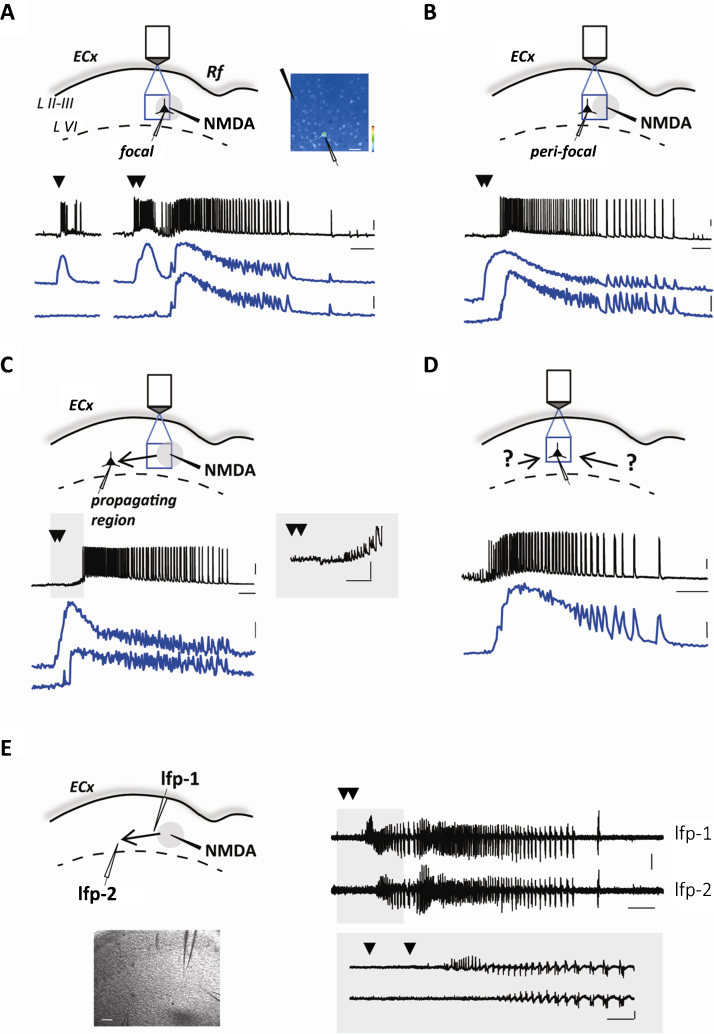
Fig. 1.
Focally induced SLDs in entorhinal cortex slice preparations from young rats. (A–C). Upper panels, schematic of the experiments with the NMDA pipette (black), the focal area (gray circle), the patched pyramidal neuron and the area of Ca2+ imaging (blue square) in rat entorhinal cortex. Lower traces, membrane potential of the pyramidal neuron (black traces) and simultaneous average Ca2+ signal from 4 putative pyramidal neurons located in the focal (upper blue traces) and peri-focal (lower blue traces) area. In A, right panel reports the Oregon-Green BAPTA-1 fluorescence with indication of the NMDA and the patch pipette (black and white, respectively). (D) Schematic of the experiment with patch recording from a pyramidal neuron and simultaneous average Ca2+ signal from 3 putative pyramidal neurons located in the same region during a spontaneous SLD. Scale bars: 20 mV; 20% ΔF/F0; 10 s (5 s for inset in (C)). Black arrowheads in this and other figures mark the NMDA pulses. E. Left panel, schematic of the experiment with two electrodes for local field potential (lfp) recording, one in the peri-focal region (250 μm) and the other distant 550 μm form the NMDA-pipette tip, and DIC image (scale bar 100 μm) of the rat brain slice during the experiment. Right traces, LFP recordings during the evoked SLD. Scale bars, 0.1 mV; 10 s. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)