Figure 2.
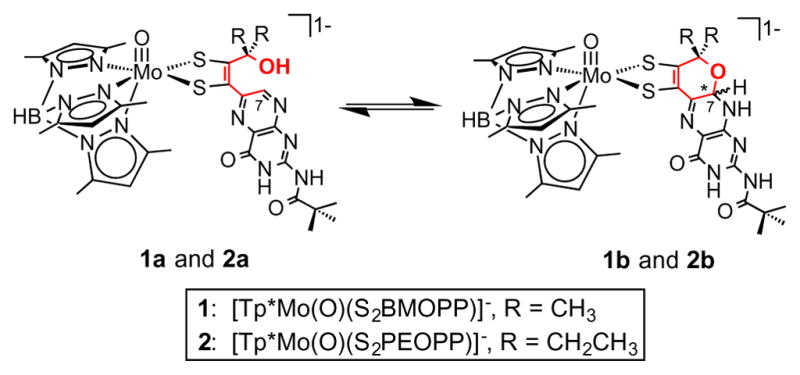
The equilibrium between the open chain forms 1a and 2a and the cyclized pyran forms 1b and 2b. The pyran ring that is involved in the tautomerism is highlighted in red. Cyclization causes the formation of two diastereomers, forming either the R or S isomer at the chiral carbon C7 marked by an asterisk.
