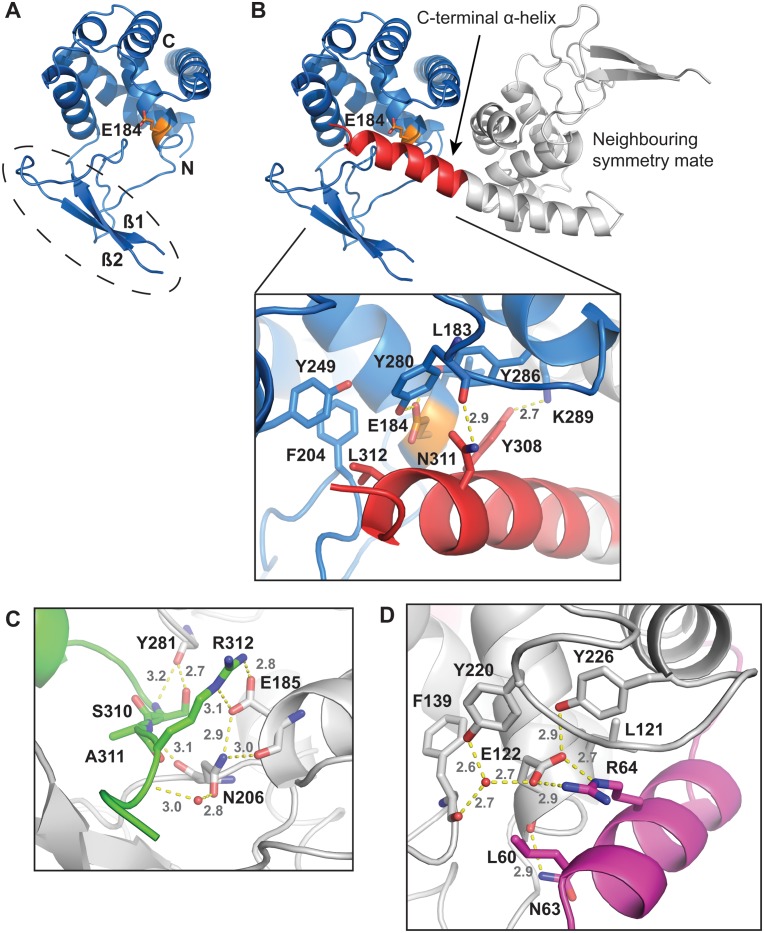
Fig 1. Structural description of StFlgJGH(151–316).
A) Cartoon diagram of the FlgJ GH domain from Salmonella typhimurium (StFlgJGH(151–316)) (blue) is shown with the catalytic glutamate (E184; orange), within the active site groove. Circled is the incomplete β-hairpin, with missing residues 223–229, that forms half of the active site groove. B) All molecules within the crystal structure were found to have their active sites blocked in trans by the C-terminal α-helix (red) of a neighbouring symmetry mate (grey) (conserved catalytic residue E184 is orange). C) In trans blockage of the GH domain active site of SpFlgJ (grey carbons) by the C-terminus of a symmetry mate (green carbons) [21,23]. D) In trans blockage of the GH domain active site of Auto (grey carbons) by the N-terminal inhibitory helix of a symmetry mate (magenta carbons) [2]. Structural models were generated using PyMol [28].