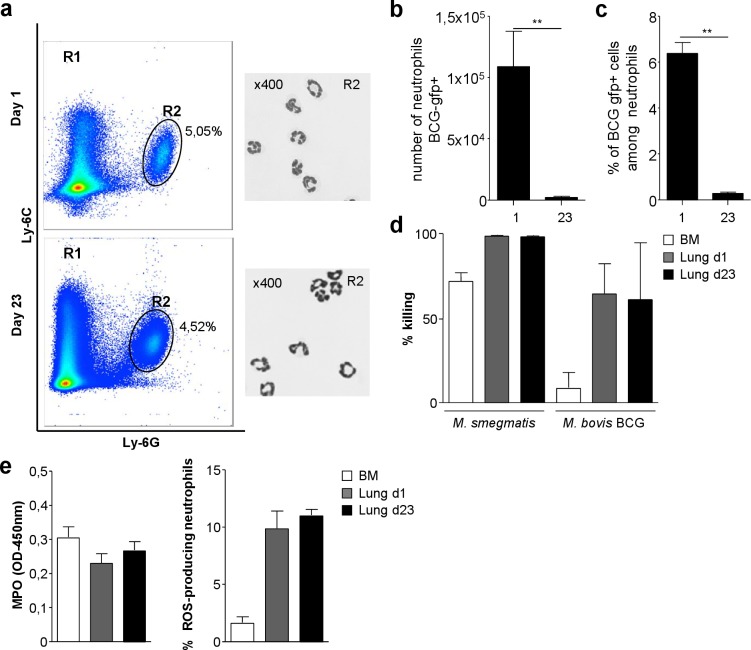
Fig 2. Day 1 or 23 lung neutrophils present similar killing abilities ex vivo.
C57BL/6 mice were infected with 5x106 CFU of BCG (a, d, e) or the green fluorescent recombinant BCG strain Myc 409 (b, c) (a) CD11b, Ly-6C, Ly-6G triple positive neutrophils recruited to the lung on day 1 or 23 were sorted by flow cytometry and stained with May Grünwald Giemsa. (b) Neutrophils carrying the green fluorescent BCG were analyzed by flow cytometry in five individual animals. Their numbers on day 1 and 23 are represented and mean +/-SD per lung. (c) In the same animals, the percentage of rBCG-gfp-infected, among all neutrophils are represented on day 1 or 23. (d) Lung neutrophils, sorted by flow cytometry at day 1 and 23 from BCG-infected mice or bone marrow neutrophils from naïve mice were infected with M. smegmatis or BCG at a MOI of 10. Bacterial killing was determined as the ratio of the initial inoculum to CFU obtained after overnight incubation with neutrophils, with 100% killing corresponding to no cell-associated bacilli. (e) The amounts of MPO and ROS bactericidal compounds produced by lung neutrophils purified at day 1 or 23 after BCG infection were compared with those produced by BM neutrophils. The results are shown as means ± SD for triplicate wells from two independent experiments (n = 6)