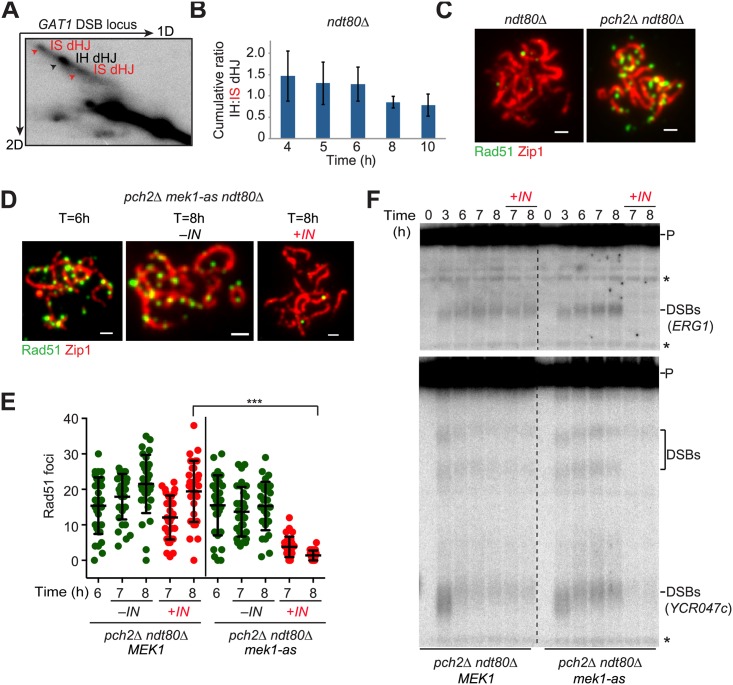
Fig 6. Mek1 activity on synapsed chromosomes suppresses DSB repair progression.
(A) Snapshot of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis to resolve interhomologue (IH) and intersister (IS) dHJ species at the GAT1 DSB locus at T = 4 h (H7036). (B) The IH:IS dHJ ratio at the GAT1 DSB hotspot at progressive meiotic time points from two independent experiments. Error bars indicate signal range. (C) Immunofluorescence analysis of Rad51 (green) and Zip1 (red) on synapsed chromosomes in the presence (H6179) or absence of PCH2 (H6639). Scale bar, 1 μm. (D-F) Cultures of pch2Δ ndt80Δ (H6639) and pch2Δ ndt80Δ mek1-as (H8360) cells were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis at T = 0 h and split at T = 6 h, after which the mek1-as inhibitor 1-NA-PP1 (IN) was added to one part of the culture to inactivate Mek1. Samples were analyzed at the indicated time points. (D) Rad51 (green) and Zip1 (red) immunofluorescence on synapsed spread chromosomes. Scale bar, 1 μm. (E) Number of Rad51 foci per spread nucleus of pch2Δ ndt80Δ MEK1 and pch2Δ ndt80Δ mek1-as cells before and after inhibitor addition to inactivate mek1-as. n = 30; error bars are S.D. from the mean; *** p < 0.001 Mann-Whitney test. (F) Southern analysis to monitor DSBs at the ERG1 (upper panel) or YCR047c (lower panel) locus. P, parental unbroken fragment; DSB, DSB sites at ERG1 and at or near the YCR047c locus; * nonspecific bands.