Figure 6.
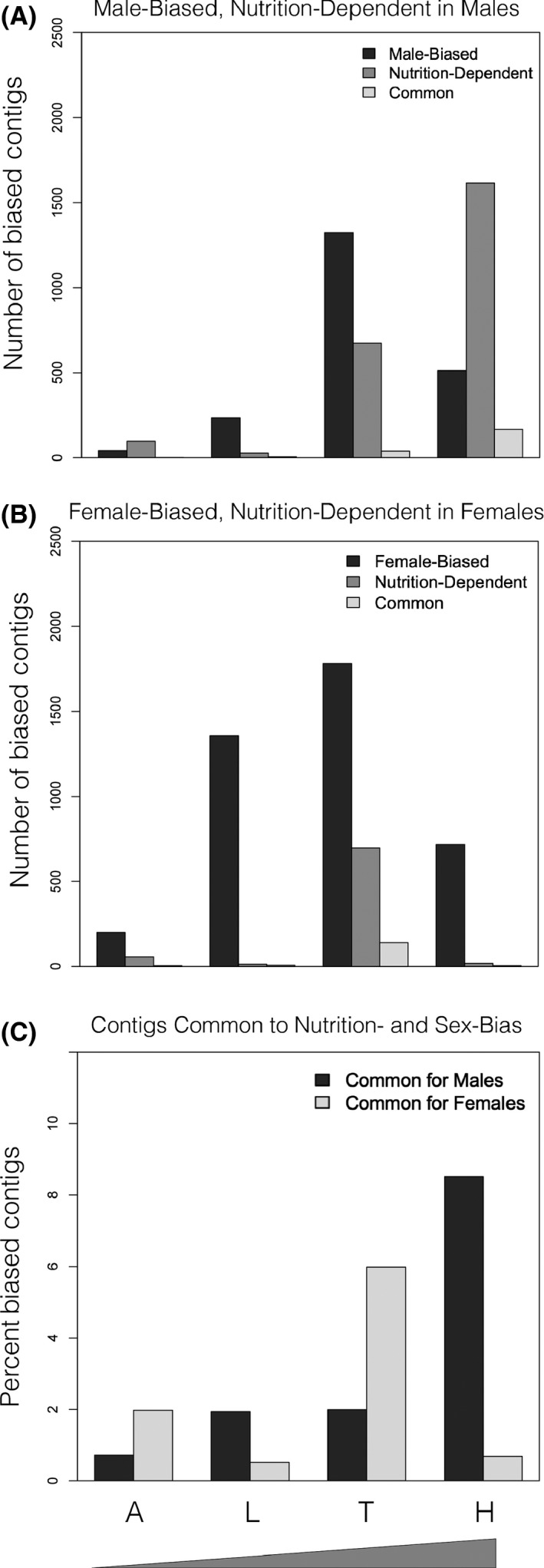
Gene expression common to nutrition dependence and sex‐bias. Sex‐biased contigs are more numerous relative to nutrition‐biased contigs, and this pattern is driven by those with higher expression in females (compare A and B). The number of contigs common to sex bias and nutrition dependence is highest in the trait that demonstrates the highest degree of nutrition‐dependent morphological sexual dimorphism and experiences sexual selection: male head horns (C; percent of the union of sex‐biased and nutrition‐dependent contigs for that tissue). The same pattern to a lesser degree in female thoracic horns (A = abdominal epidermis; L = leg epidermis; T = thoracic horn epidermis; H = head horn epidermis). Ramp on x‐axis indicates the increasing degree of sexual dimorphism among focal traits.
