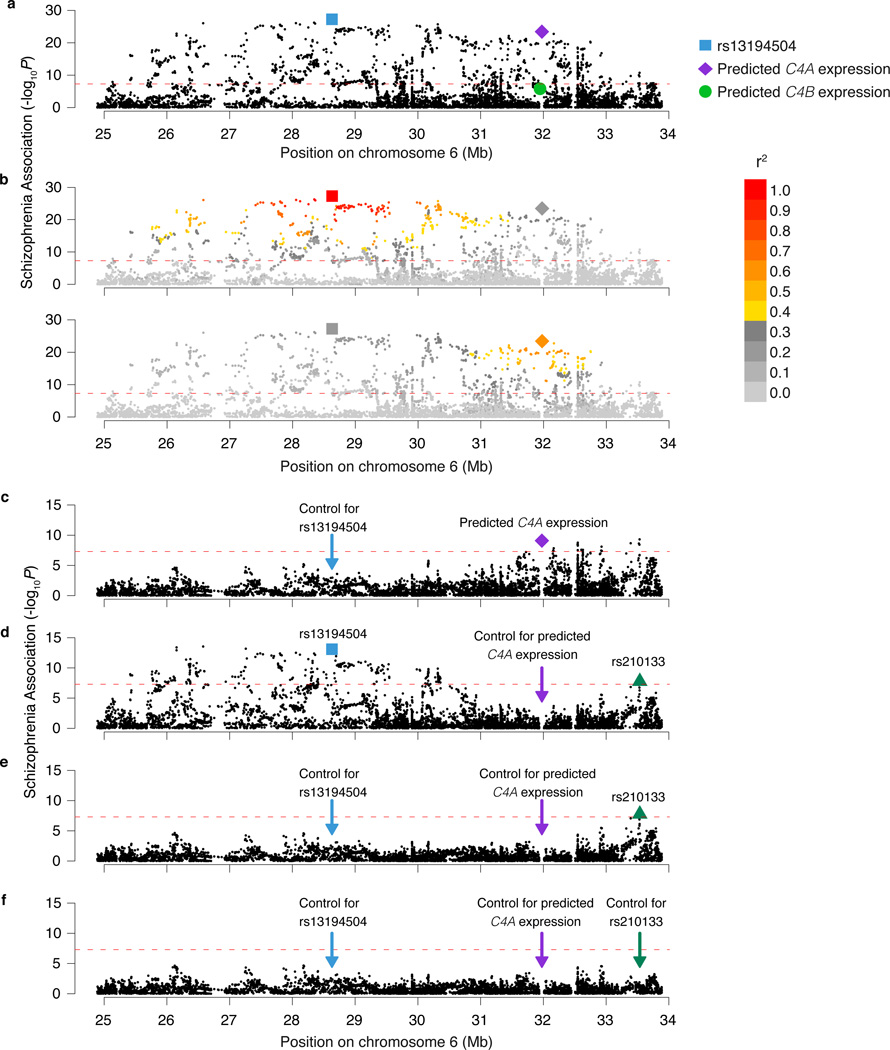
Figure 4. Association of schizophrenia to C4 and the extended MHC locus.
Association of schizophrenia to 7,751 SNPs across the MHC locus and to genetically predicted expression levels of C4A and C4B in the brain (represented in the genomic location of the C4 gene). The data shown are based on analysis of 28,799 schizophrenia cases and 35,986 controls of European ancestry from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. The height of each point represents the statistical strength (−log10(p)) of association with schizophrenia.
(a, b) Association of schizophrenia to SNPs in the MHC locus and to genetically predicted expression of C4A and C4B. In (b), genetic variants are colored by their levels of correlation to rs13194504 (upper panel) or by their levels of correlation to genetically predicted brain C4A expression levels (lower panel).
(c–f) Conditional association analysis. The red dashed line indicates the statistical threshold for genome-wide significance (p = 5×10−8).
See also Extended Data Fig. 5–7 for detailed association analyses involving C4 locus structures and HLA alleles.