Fig. 2.
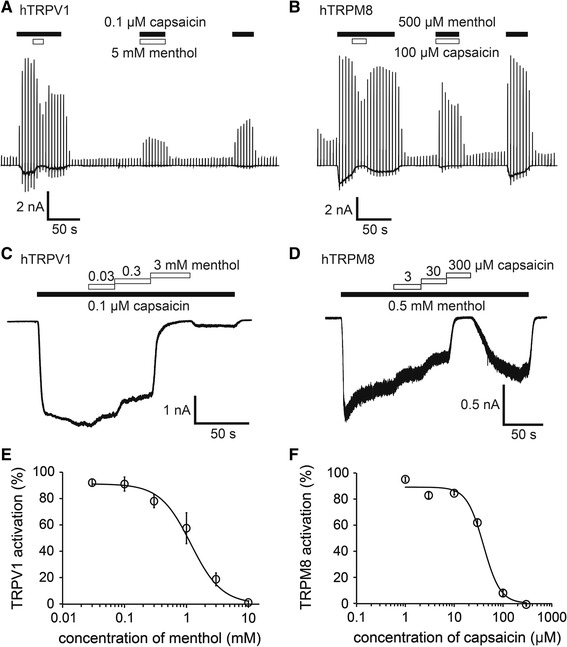
Inhibition of hTRPV1-mediated currents by menthol and inhibition of hTRPM8-mediated currents by capsaicin in HEK293T cells. a A representative trace of the whole cell showing that 0.1 µM capsaicin-evoked hTRPV1 currents were inhibited by menthol (5 mM) in the presence of extracellular Ca2+. b A representative trace of the whole cell showing that 500 µM menthol-evoked hTRPM8 currents were inhibited by 100 µM capsaicin in the presence of extracellular Ca2+. c A representative 0.1 μM capsaicin-evoked hTRPV1 current that was inhibited by menthol in a dose-dependent manner in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. d A representative 0.5 mM menthol-evoked hTRPM8 current that was inhibited by capsaicin in a dose-dependent manner in the absence of extracellular Ca2+. e Dose-dependent inhibition of 0.1 μM capsaicin-evoked hTRPV1 current by menthol. the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) and Hill’s coefficient values are 1.2 ± 0.2 mM and 1.7 ± 0.3, respectively (n = 5–8). f Dose-dependent inhibition of 0.5 mM menthol-evoked hTRPM8 current by capsaicin; the IC50 and Hill’s coefficient values are 39.9 ± 6.4 µM and 2.5 ± 0.7, respectively (n = 6–8). Data are shown as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM)
